An extension with rich support for Jupyter
- Install the extension
- When using Python, install the Python extension as well.
- Install Jupyter
- You're ready to use it.
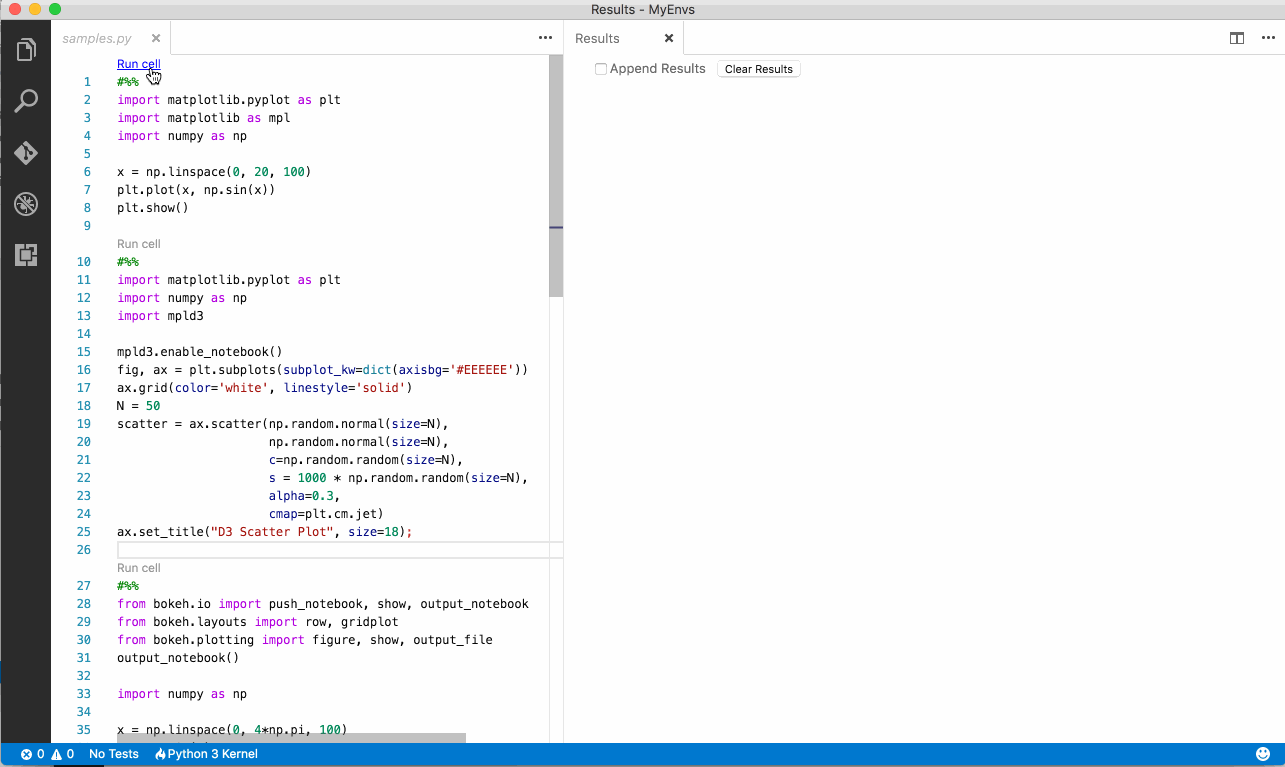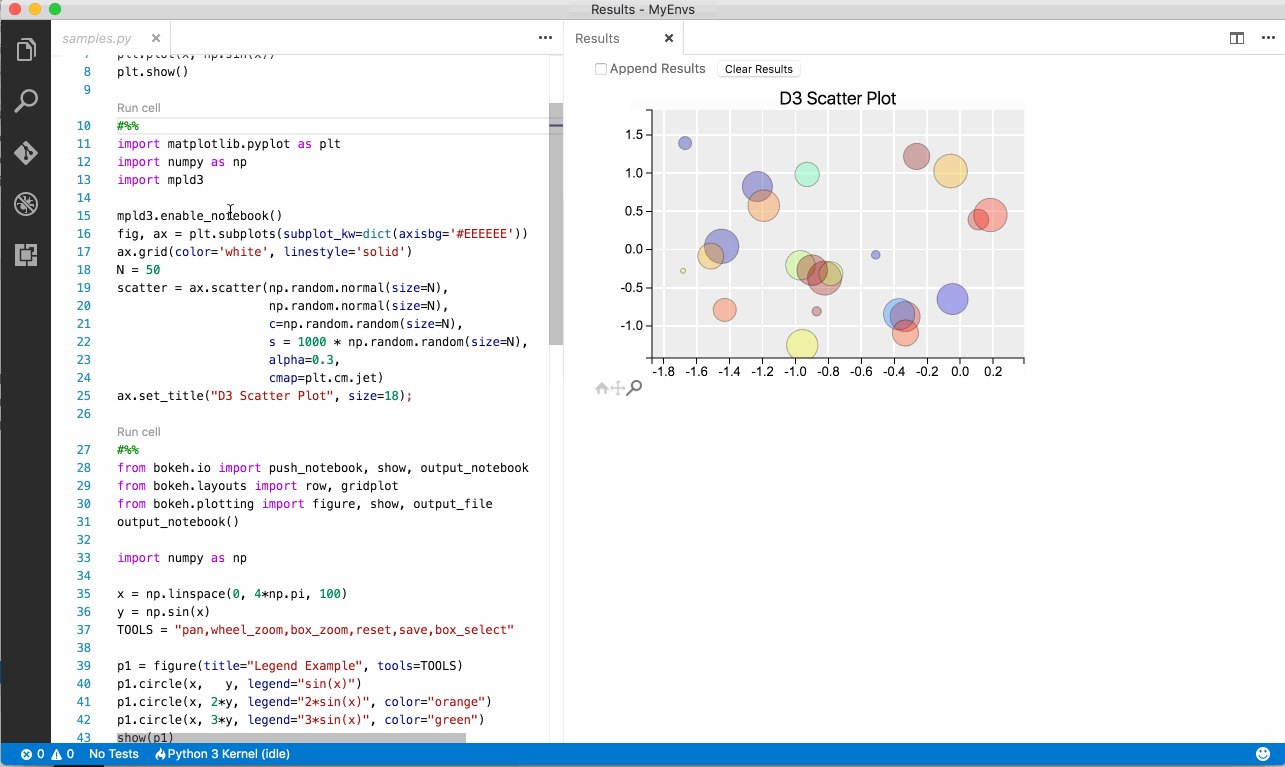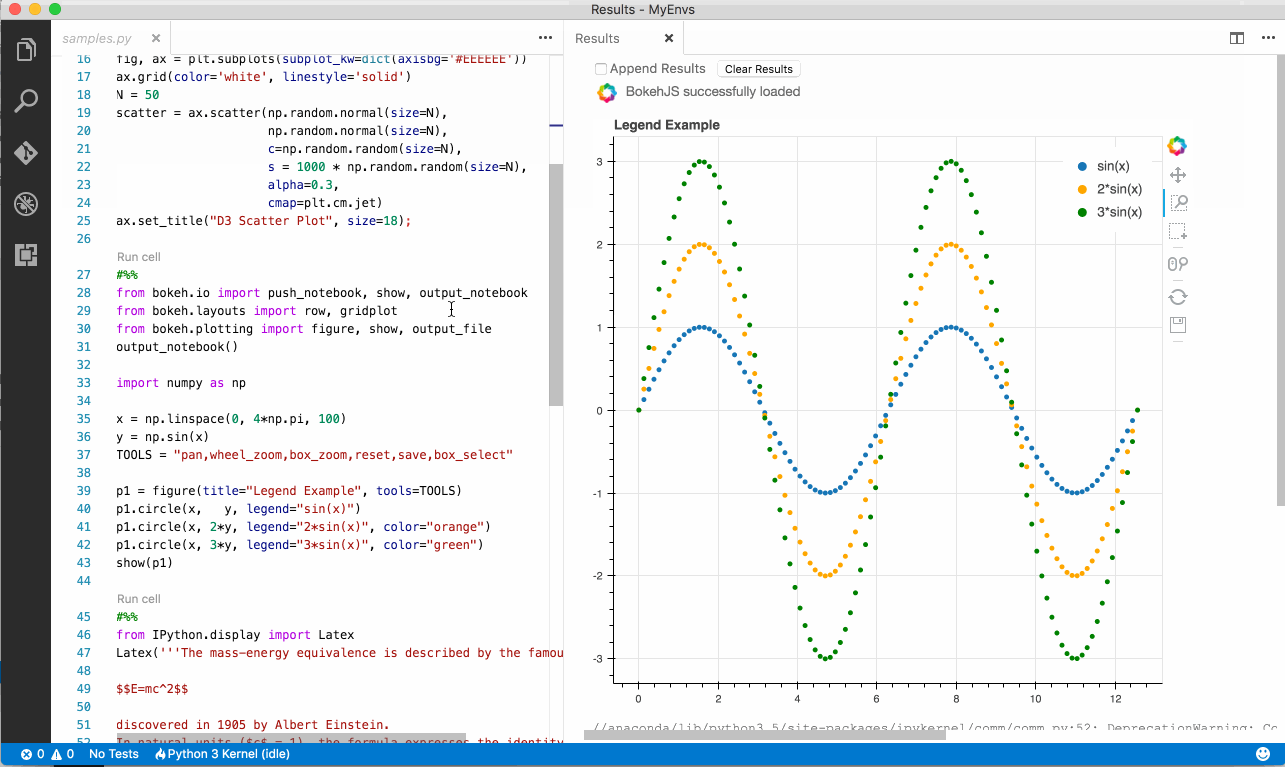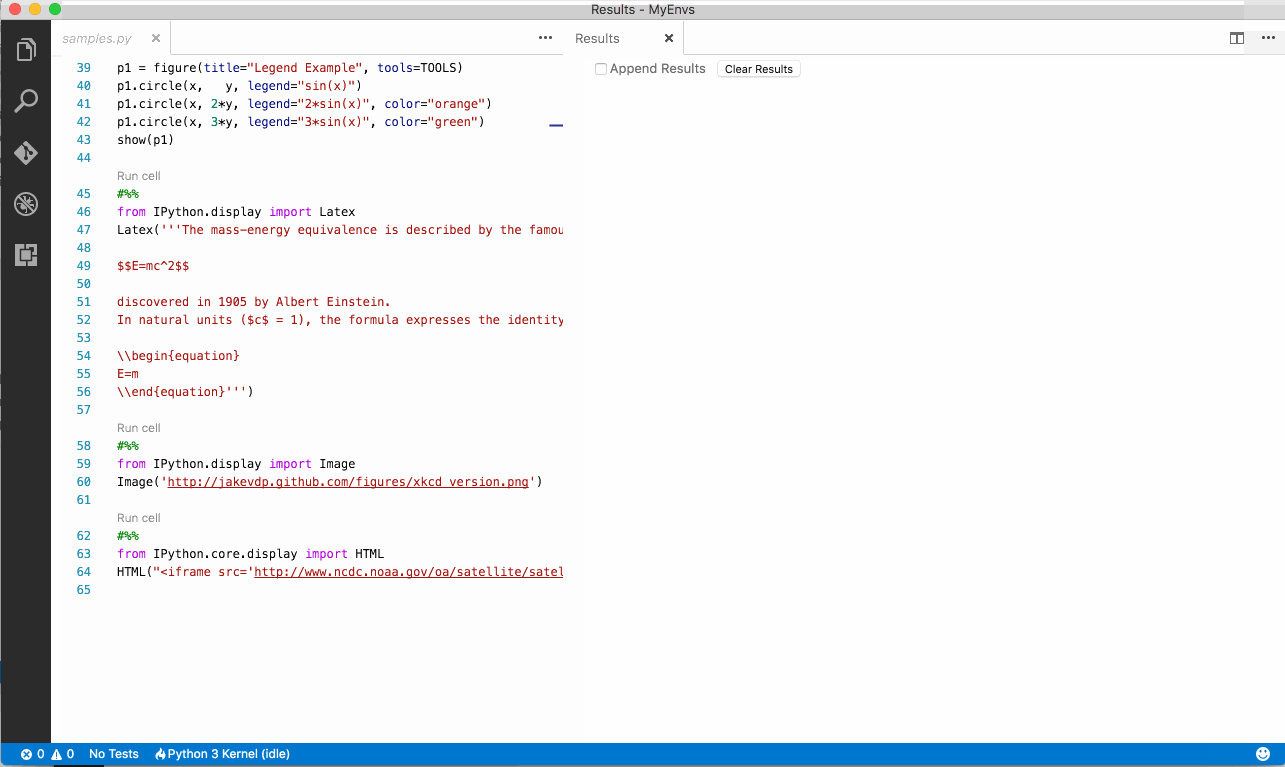
- Create a Python file with the following text
#%%
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(0, 20, 100)
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x))
plt.show() - Click on the code lens
Run Cell
- If you want to run cell with Ctrl+Enter, add those code in keybindings.json.
{ "key": "ctrl+enter", "command": "jupyter.execCurrentCell",
"when": "editorTextFocus"
}Try this to connect to a remote Jupyter kernel running on a server, or inside Docker container:
- Make sure Jupyter, Notebook, and jupyter_kernel_gateway packages are installed. They are all included by default in Anaconda installation, but if you are using PIP you may need to install them manually.
- Run following commands on Linux: (Windows users will need to adapt these commands for their env)
# Generate config file for KernelGateway
jupyter kernelgateway --KernelGatewayApp.generate_config=True
# Generate config for Jupyter Notebook
jupyter notebook --generate-config --allow-root
# Append appropriate values to both config files
echo -e "c.JupyterWebsocketPersonality.list_kernels = True" >> ~/.jupyter/jupyter_kernel_gateway_config.py
echo -e "c.NotebookApp.allow_root = True" >> ~/.jupyter/jupyter_notebook_config.py
- Start a remote Jupyter Notebook or headless KernelGateway
- Find the token in the output of the Jupyter server logs: http://jupyter-notebook.readthedocs.io/en/latest/security.html
Then in VS Code:
- ctrl+shift+p
- Jupyter: Enter the url of local/remote Jupyter Notebook
- Select existing kernels from the drop-down list, or start a new kernel
- Select language for the kernel from drop-down list: e.g., "Python 3"
For further information and details continue through to the documentation.
- Contributions are always welcome. Fork it, modify it and create a pull request.
- Any and all feedback is appreciated and welcome.
- Notebook not detected #46
- Fix high CPU usage #40
- Bug fix (extension fails to load)
- Increase timeout waiting for Jupyter Notebook to start
- Preliminary support for older versions of Jupyter Notebook (< 4.2.0)