OTP or One Time Password is a one-time use password that has a certain validity period. Generally the validity period is made very short and only gives the chance to the recipient to enter it into the application and send it to the application server that requires it. OTP is strictly confidential so the clear text of the OTP should not be stored by any party. In fact, the application server only stores the hash or token that matches the OTP. Clear text is only generated and then sent to the recipient. In other words, clear text is only known to the OTP recipient.
The most popular OTPs are sent via SMS or Short Message Service. The use of SMS has the following advantages:
- Can only be received by the device where the SIM card is installed. This of course comply
What you haverule inmultifactor authentication - Easily readable on almost all makes and models of mobile phone devices
- Generally the device immediately notifies the presence of an incoming message without requiring user action
- On smartphone devices, applications can directly read the message if permitted by the user. Thus, the application can directly verify the OTP without requiring manual action from the user. This will save time and reduce errors
- Does not require the recipient's credit so that the recipient of the message does not have to pay anything to be able to receive the message
- Has a very wide range
- SMS receiving devices are available in various price classes so that they can be reached by almost all people
Of the many advantages above, it turns out that SMS has limitations. SMS must be sent through a telecommunications operator legally registered in the sending country. SMS can be sent using a GSM device connected to a telecommunications operator. The cheapest devices for sending SMS are cell phones and modems. In addition, the sender must pay a service fee to the telecommunications operator. This fee will be shared to all operators involved in sending SMS.
Another way to send SMS is by working directly with telecommunications operators or using third party services. Cooperation with telecommunications operators is certainly not easy. In addition to having a legal entity, the costs required are of course not small. In addition, the volume of SMS sending is also a consideration for whether the cooperation is accepted or not by the telecommunications operator. The use of third party services is another option. The safety factor is of course a consideration. The service provider must of course be trusted to maintain the confidentiality of the OTP sent.
For small-scale companies who want to build their own OTP delivery system, they can use a variety of applications that are available for free or paid in the market. Some considerations in choosing an OTP application are as follows:
- Delivery speed
- Security/confidentiality
- Ease of installation and integration
- Initial costs and operational costs
Applications that use a database to connect between the receiving side of the message and the GSM modem are of course not secure. The data in the database can be read by the administrator. In fact, administrators can request OTP when the user is not aware of it and is not transacting.
Applications that require the use of a public IP address of course do not provide flexibility for users. Companies or individuals who do not subscribe to the internet with a public IP cannot use the application. Users need to place the server on a network with a public IP.
Applications that run on desktops and laptops of course require high investment and operational costs. The laptop or desktop that is used must operate 24 hours a day and 7 days a week. Of course, the electricity used is not small.
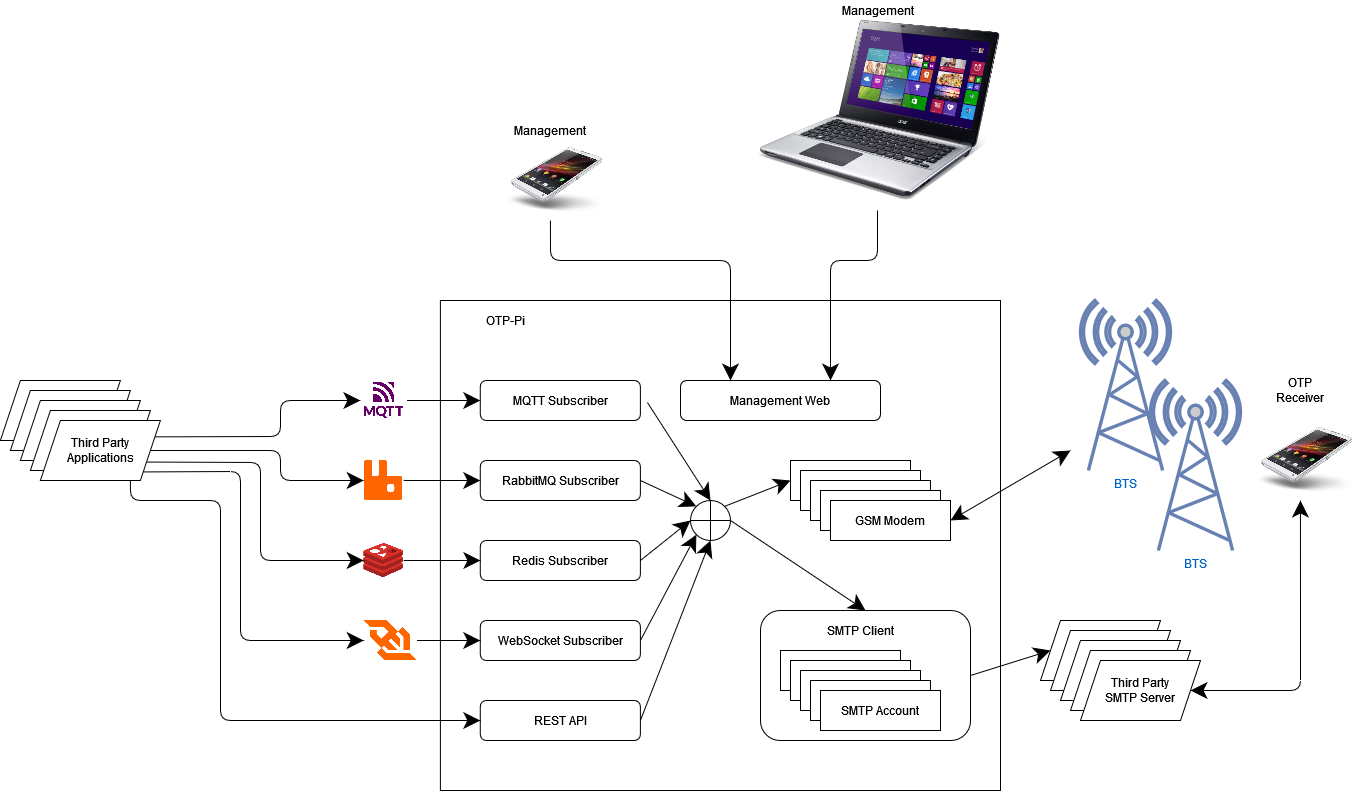
OTP-Pi answers all of the above challenges. With a very cheap device, users can have an SMS gateway that provides many features and can be operated at a very low cost.
OTP-Pi is a server for sending SMS via HTTP, WebSocket and Message Broker protocols. Users can install OTP-Pi on the server with a static IP address that can be accessed by clients who will send SMS. In addition, users can also install OTP-Pi on servers with dynamic IP addresses. This server then accesses a websocket server, RabbitMQ server or Mosquitto server. OTP-Pi acts as a consumer that will send all SMS it receives.
To publish message using PHP to RabbitMQ, Mosquitto and Redis, see example on https://github.com/kamshory/OTP-Publisher
OTP-Pi does not require an RDBMS. All data is stored in RAM and file system. The OTP-Pi also does not store the sent OTP. This will increase the security and confidentiality of the OTP.
- Raspberry Pi 3 Model B or higher.
- Minimum RAM is 1 GB.
- SD Card minimum is 16 GB. 32 GB SD Card is recommended.
- Power supply 5 Volt 3 Ampre to prevent the Raspberry Pi from operating with under voltage.
- RTC DS3231 installed on Raspberry Pi.
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 1.8 or Java Development Kit (JDK) 1.8.
OTP-Pi comes with built-in wifi. The built-in wifi is used to configure the device so that the OTP-Pi can be installed on your wired network. The built-in wifi is also useful when you are going to reset the OTP-Pi configuration.
User can send OTP with several methods. OTP-Pi allow user to create and validate OTP via REST API or just send SMS or email contains OTP code via RabbitMQ, Redis, Mosquitto, ActiveMQ and WebSocket.
| Method | Send SMS | Send Email | Block MSISDN | Unblock MSISDN | Create OTP | Validate OTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REST API | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| WebSocket | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Require callback |
| RabbitMQ* | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Require callback |
| Redis* | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Require callback |
| Mosquitto* | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Require callback |
| ActiveMQ* | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Require callback |
| Stomp* | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Require callback |
If you wish all features to be enable from API, you can use OTP-Publisher. Clone https://github.com/kamshory/OTP-Publisher to get it.
Vendors
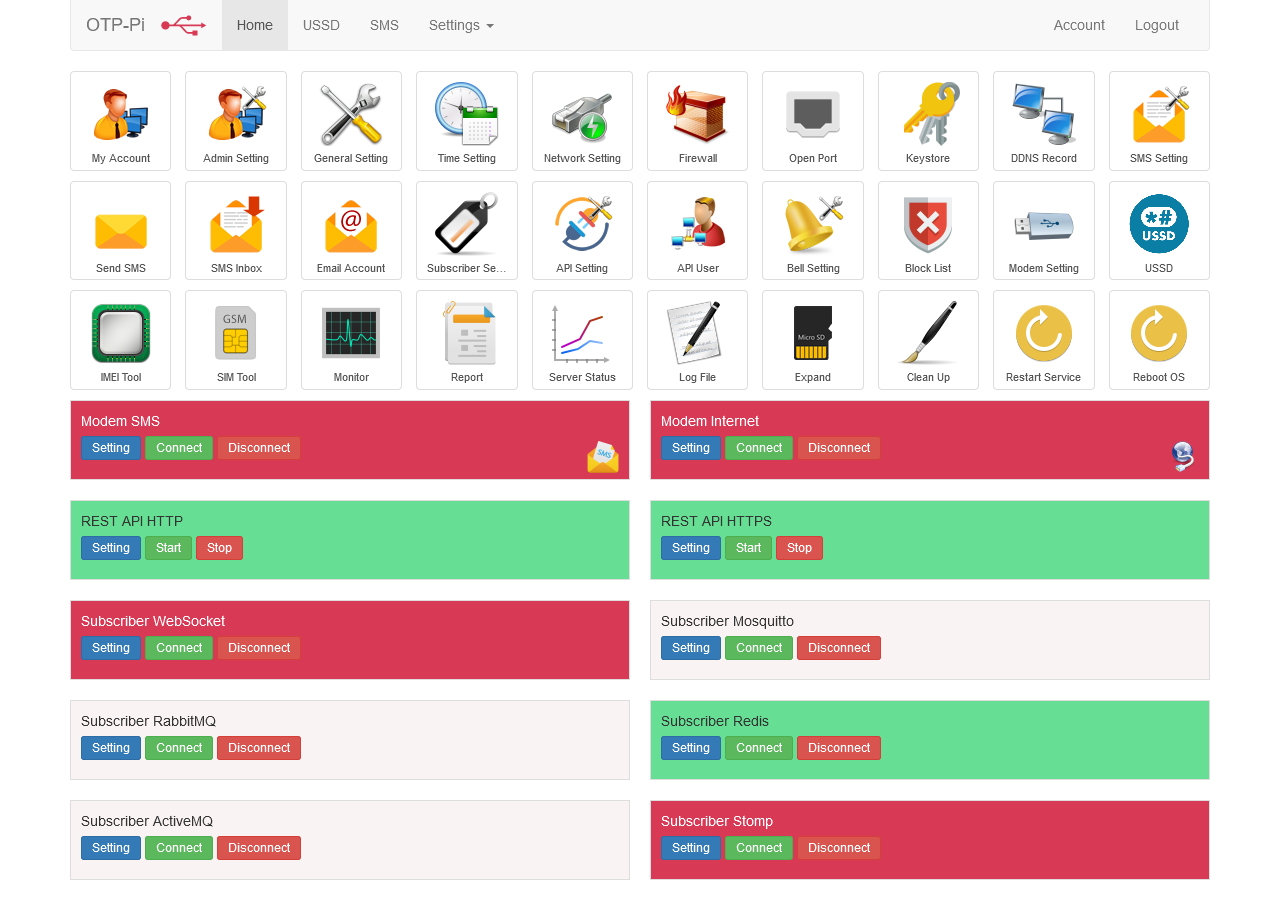
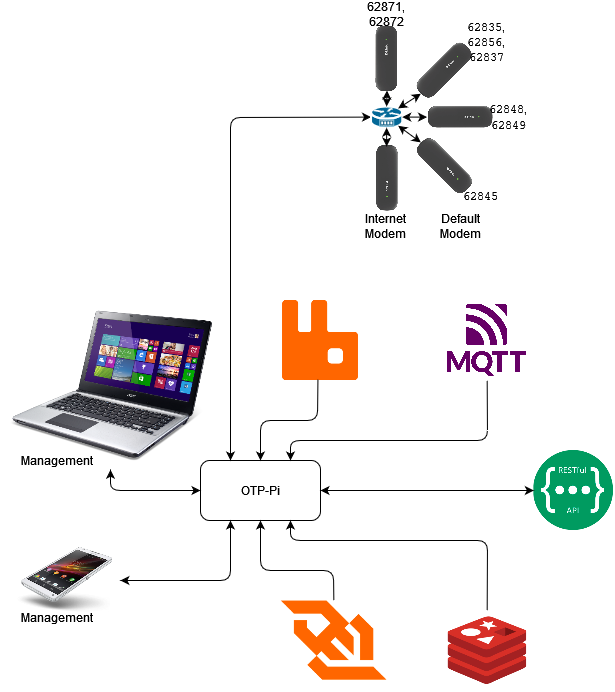
Modem is a list of modems installed on the OTP-Pi. Modems are named based on the make and model of the device and the connection used. The modem can be turned on and off at any time. An inactive modem will not be used to send SMS even if it is physically attached to the OTP-Pi and receiving power.
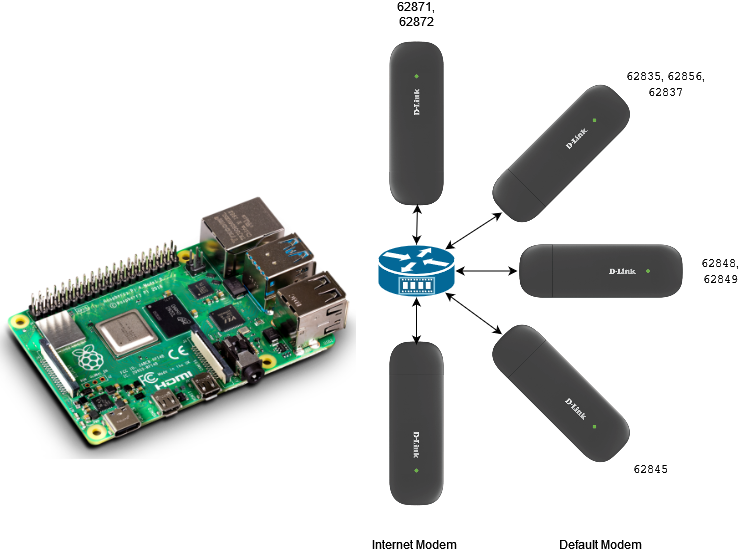
OTP-Pi can use multiple modems at once. By default, the OTP-Pi can use up to 4 modems at once without the need for additional devices. The use of a hub is possible so that users can use more than 4 modems in one OTP-Pi device. The modems are registered as usual. Sending SMS will use the Round-Robin algorithm where all active modems will be used in rotation.
OTP-Pi will periodically check all serial ports on the server. If a device change is detected, the OTP-Pi will check the list of pre-set modems. If the port is used on one of the modems on the list, the OTP-Pi will update the modem connection status. In addition, OTP-Pi will also display a notification on the administrator screen.
In reality, cost efficiency becomes very important for users. The cost of sending SMS should be reduced as much as possible. Telecommunications operators usually apply lower cost when sending SMS to subscriber numbers of the same telecommunications operator. On the other hand, the cost of sending SMS will be higher when sending SMS to customer numbers from other operators.
OTP-Pi allows users to set up SMS sending. For example: a user uses 4 modems with 4 different SIM cards from different telecommunication operators.
- Modem 1 with SIM Card from Telecommunications Operator 1
- Modem 2 with SIM Card from Telecommunications Operator 2
- Modem 3 with SIM Card from Telecommunications Operator 3
- Modem 4 with SIM Card from Telecommunications Operator 4
Telecommunications Operator 1 applies a fee of IDR 50 for numbers with prefixes 62871 and 62872 and applies a fee of IDR 350 for numbers other than that.
Telecommunications Operator 2 applies a fee of IDR 100 for numbers with prefixes 62835, 62856, and 62837 and applies a fee of IDR 350 for numbers other than that.
Telecommunications Operator 3 applies a fee of IDR 60 for numbers with the prefix 62845 and applies a fee of IDR 250 for numbers other than that.
Telecommunications Operator 4 applies a fee of IDR 90 for numbers with prefixes 62848 and 62849 and applies a fee of IDR 200 for numbers other than that.
From the case above, the lowest cost for other operators is IDR 200. Users can set modem 4 as the default modem. All SMS other than the prefixes 62871, 62872, 62835, 62856, 62837 and 62845 will use this modem and are sent via Telecommunications Operator 4. All SMS for numbers with prefixes 62871 and 62872 uses modem 1 and is sent via Telecommunication Operator 1. All SMS for numbers with prefix 62835, 62856, and 62837 use modem 2 and are sent via Telecommunication Operator 2. All SMS for numbers with prefix 62845 use modem 3 and sent via Telecommunication Operator 3. Thus, the cost of sending SMS will be reduced.
Users can use 2 or more SIM cards from the same operator. The modem will be used interchangeably with the Round-Robin algorithm when OTP-Pi sends SMS to numbers with the same prefix.
The cost of sending SMS will be even lower when the user takes advantage of the promo from the telecommunications operator in question. Some operators will apply very low SMS sending fees after the user sends several SMS with certain conditions.
Prefix setting using MSISDN. Thus, in the example above, when a user in Indonesia sets the prefix 0871, it stores 62871. Thus, the user must use the prefix length of 5 instead of 4.
OTP-Pi allows users to perform USSD commands on individual modems. The USSD command, of course, depends on each telecomunications operator used on each SIM card installed on each modem.
Manual SMS is used to test whether each modem can send SMS.
The OTP-Pi can connect to the internet using a mobile modem. Thus, users do not need to connect the OTP-Pi with wired or optical internet. It provides an alternative for users in choosing an internet connection.
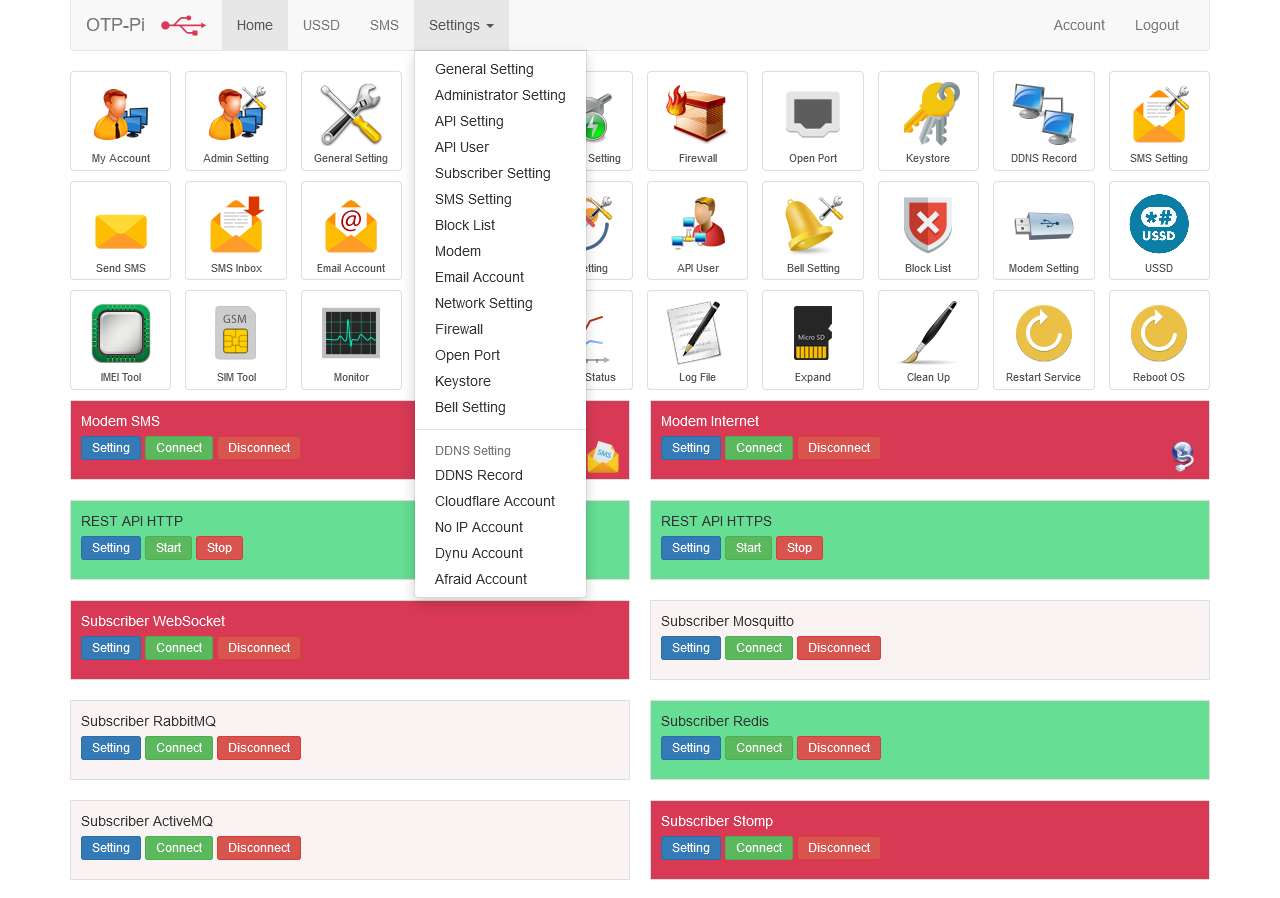
Administrator Settings is a menu to configure administrator. New OTP-Pi devices don't have an administrator yet. The user must create an administrator first before using it. Please enter the OTP-Pi access point according to the SSID and password listed on the brochure and scan the QR Code on the brochure using a smartphone.
The default address of administration web is http://192.168.0.11:8888
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Username | Administrator identifier when logging in to OTP-Pi |
| Password | Administrator's security when logging into OTP-Pi |
| Phone Number | The phone number can be used if the administrator forgets the password. Password will be sent via SMS. Of course this can only be done when the OTP-Pi has been configured correctly |
Email can be used if the administrator forgets the password. Password will be sent via email. Of course this can only be done when the OTP-Pi has been configured correctly.
API Setting is a REST API configuration for sending SMS.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| HTTP Port | The server port for HTTP |
| Enable HTTP | Setting to enable or disable HTTP port |
| HTTPS Port | he server port for HTTPS |
| Enable HTTPS | Setting to enable or disable HTTPS port |
| Message Path | The path to send SMS and email |
| Blocking Path | Path to block a phone number so that OTP-Pi does not send SMS to that number |
| Unblocking Path | Path to unblock a phone number so that OTP-Pi can send SMS to that number again |
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Device Name | The device name of OTP-Pi |
| OTP Expiration | OTP expiration in mili second. It will be used when sender not send expiration on the OTP. OTP-Pi will not forward expire OTP.* |
| Drop Expire OTP | Flag that OTP-Pi will drop or ignone the expire OTP.* |
| Device Time Zone | The device time zone. Select one of the time zone listed |
| NTP Server | NTP server address to update the device time |
| Update Timer | Time to update the device time. Set to Never if the device is offline |
| Inspect Modem Connection | Time to update the modem connection. Set to Never if will not inspect the modem connection |
| Restart Service | Time to restart the service. Set to Never if you will not restart the device periodically |
| Restart Device | Time to reboot the device. Set to Never if you will not reboot the device periodically |
*) Under abnormal conditions, the OTP may be delayed on the message broker and received by the OTP-Pi after expiration. OTP-Pi can ignore expired OTPs to avoid junk delivery. If the sender does not include expiration in the OTP, the expiration time will be calculated from date_time plus milliseconds in OTP Expiration. If the sender includes expiration in the OTP, the OTP-Pi will use that time.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Device Time | Device time |
| Device Time Zone | The device time zone. Select one of the time zone listed |
| NTP Server | NTP server address to update the device time |
| Update Timer | Time to update the device time. Set to Never if you will not restart the device periodically |
API User is an account that sends SMS via REST API.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Username | Username is the sender identifier when sending SMS to OTP-Pi |
| Email is contact information in the form of email addresses of API users | |
| Phone Number | Phone number is contact information in the form of phone numbers from API users |
| Password | Username is the sender's security when sending SMS to OTP-Pi |
OTP-Pi provides an option if this device is installed on a mobile internet network or on a network where the sending device may not be able to reach the address of the OTP-Pi. Users can send OTP with message broker as follows:
- RabbitMQ (AMQP)
- Mosquitto (MQTT)
- Redis
- ActiveMQ
- Stomp
- WSMessageBroker (WebSocket)
WSMessageBroker
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable | Enable or disable WSMessageBroker subscribsion |
| SSL | SSL connection |
| Host | WSMessageBroker host name or IP address |
| Port | Port number |
| Path | Context path |
| Username | Username on basic authorzation |
| Password | Password on basic authorzation |
| Topic | Topic or channel of subscribsion |
| Timeout | Request time out |
| Reconnect Delay | Delay to reconnect |
| Refresh Connection | Refresh WebSocket connection |
RabbitMQ
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable | Enable or disable RabbitMQ subscribsion |
| SSL | SSL connection |
| Host | RabbitMQ host name or IP address |
| Port | Port number |
| Version | AMQP version |
| Username | RabbitMQ username |
| Password | RabbitMQ password |
| Topic | Topic or channel of subscribsion |
| Timeout | Request time out |
| Reconnect Delay | Delay to reconnect |
| Refresh Connection | Refresh RabbitMQ connection |
Mosquitto
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable | Enable or disable Mosquitto subscribsion |
| SSL | SSL connection |
| Host | Mosquitto host name or IP address |
| Port | Mosquitto port number |
| Client ID | Client ID |
| Username | Username |
| Password | Password |
| Topic | Topic or channel of subscribsion |
| QoS | QoS of the subscribsion |
| Timeout | Request time out |
| Reconnect Delay | Delay to reconnect |
| Refresh Connection | Refresh Mosquitto connection |
Redis
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable | Enable or disable Redis subscribsion |
| SSL | SSL connection |
| Host | Redis host name or IP address |
| Port | Redis port number |
| Username | Client ID |
| Password | Redis password (if present) |
| Topic | Topic or channel of subscribsion |
| Timeout | Request time out |
| Reconnect Delay | Delay to reconnect |
| Refresh Connection | Refresh Redis connection |
Stomp
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable | Enable or disable Stomp subscribsion |
| SSL | SSL connection |
| Host | Stomp host name or IP address |
| Port | Stomp port number |
| Username | Username |
| Password | Password |
| Topic | Topic or channel of subscribsion |
| Timeout | Request time out |
| Reconnect Delay | Delay to reconnect |
| Refresh Connection | Refresh Stomp connection |
ActiveMQ
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable | Enable or disable ActiveMQ subscribsion |
| SSL | SSL connection |
| Host | ActiveMQ host name or IP address |
| Port | ActiveMQ port number |
| Client ID | Client ID |
| Username | Username |
| Password | Password |
| Topic | Topic or channel of subscribsion |
| Timeout | Request time out |
| Refresh Connection | Refresh ActiveMQ connection |
SMS Setting is the configuration of sending SMS by OTP-Pi.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Country Code | Phone country code (numeric). See https://countrycode.org/ |
| Recipient Prefix Length | For Indonesia, use 5 |
| Log Outgoing SMS | Flag to log outgoing SMS |
| Monitor SMS Traffic | Flag to monitor SMS traffic |
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Modem Name |
| Port | Serial port used |
| Manufacturer | Manufacturer identification |
| Model | Device model |
| Revision | Device revision |
| IMEI | Modem IMEI |
| IMSI | IMSI of the SIM Card used |
| Operator | Telecommunication operator |
| MSISDN | MSISDN of the SIM Card used |
| SMS Center | SMS center |
| Recipient Prefix | Recipient prefix that will receive SMS from this modem. See Prefix-Based Routing secton |
| SIM Card PIN | SIM Card PIN if exists |
| Baud Rate | Modem baud rate |
| Parity Bit | Modem parity bit |
| Start Bits | Modem start bits |
| Stop Bits | Modem stop bits |
| Internet Access | Use modem to connect to the internet |
| APN | Access Point Name |
| APN Username | Username of the APN to connect to the internet |
| APN Password | Password of the APN to connect to the internet |
| Dial Number | Number to be dialed to connect to the internet |
| Init Dial 1 | Initial AT command to be executed to connect to the internet |
| Init Dial 2 | Initial AT command to be executed to connect to the internet |
| Init Dial 3 | Initial AT command to be executed to connect to the internet |
| Init Dial 4 | Initial AT command to be executed to connect to the internet |
| Init Dial 5 | Initial AT command to be executed to connect to the internet |
| Dial Command | Command to be executed to connect to the internet |
| Send SMS from API | Flag that the modem will be used to send SMS from API or not. If it set to false, modem will not send incomming SMS from API but user can send SMS manualy from the management web. |
| Default Modem | Flag that the modem is default or not. The default modem will be used to send SMS that the prefix is not exists on Recipient Prefix of the other modems. |
| Active | Flag for the modem that will be used or not |
| Operator | APN | Username | Password | Dial UP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Telkmonsel | internet | *99# | ||
| XL | internet | *99# | ||
| Three | 3data | 3data | 3data | *99# |
| Smartfren | smart | smart | smart | #777 |
| Indosat Ooredoo | indosatgprs | *99# | ||
| Axis | axis | axis | 123456 | *99# |
Blocking list is a list of blocked phone numbers. Blocked numbers will not receive SMS from any modem. This list can be added and whitened via the REST API, abbitMQ, Mosquitto and WebSocket. This list can also be manually added, whitened, or deleted via the web admin.
OTP-Pi supports multiple email accounts. Email account is a configuration that contains SMTP Server address, SMTP server port, username, password, and other configurations.
SMTP Server is used to send OTP to email addresses and can be used to reset passwords.
The use of multiple email accounts is recommended because the number of emails sent by each email account will decrease. For example: an SMTP server limits 500 emails per day. Using 20 email accounts, OTP-Pi can send up to 10,000 emails per day.
To use Gmail SMTP, use the following configuration:
Use Port 587
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| SMTP Host | smtp.gmail.com |
| SMTP Port | 587 |
| SSL Enable | No |
| Start TLS Before Send | Yes |
| Authentication | Yes |
| Sender Account | Gmail Account |
| Sender Password | Gmail Password |
| Active | Yes |
Use Port 465
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| SMTP Host | smtp.gmail.com |
| SMTP Port | 465 |
| SSL Enable | Yes |
| Start TLS Before Send | Yes |
| Authentication | Yes |
| Sender Account | Gmail Account |
| Sender Password | Gmail Password |
| Active | Yes |
See https://mkyong.com/java/javamail-api-sending-email-via-gmail-smtp-example/
The OTP-Pi is equipped with a passive buzzer. The passive buzzer will make a sound when an undesirable condition occurs. The user can set any conditions that will cause the buzzer to make a sound.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Fail Send SMS | Bell on SMS failure |
| AMQP Disconnected | Bell on RabbitMQ disconnected |
| MQTT Disconnected | Bell on Mosquitto disconnected |
| WS Disconnected | Bell on WebSocket disconnected |
DDNS Records are records for dynamic DNS settings. DDNS or Dymanic Domain Name System is a DNS setting mechanism that is done repeatedly because the public IP address of the server is always changing.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Provider | DNS server provider or vendor |
| Type | Record type. Currently only support A Record |
| Zone | Zone or domain name |
| Record Name | Record name or subdomain |
| TTL | Time to leave |
| Proxied | For Cloudflare only. It will use Cloudflare proxy and cache or not |
| Update DNS | Interval to update DNS. OTP-Pi will update it by sending request to the DNS server provider |
| Force Create Zone | For Cloudflare only. It will create zone if not exists |
| Active | Flag that DDNS record is active or not |
OTP-Pi provides DDNS setup using DDNS vendor. Some of the supported DDNS vendors are as follows:
- Cloudflare - https://www.cloudflare.com/
- NoIP - https://www.noip.com/
- Dynu Dyn DNS - https://www.dynu.com/
- Free DNS Afraid - https://freedns.afraid.org/
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloudflare Endpoint | Cloudflare endpoint |
| Account ID | Cloudflare account ID |
| Cloudflare email | |
| API Key | Cloudflare API key |
| Token | Cloudflare Token |
| Active | Flag that this Cloudflare account is active or not |
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| No IP Endpoint | No IP endpoint |
| Username | No IP username |
| Password | No IP password |
| Company Name | Your nompany name |
| Maintainer Email | Maintainer email or your company |
| Active | Flag that this No IP account is active or not |
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| API Version | Dynu API version |
| Dynu Endpoint | Dynu endpoint |
| API Key | Dynu API key |
| Username | Dynu username |
| Password | Dynu password |
| Company Name | Your nompany name |
| Maintainer Email | Maintainer email or your company |
| Active | Flag that this Dynu account is active or not |
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Afraid Endpoint | Free DNS Afraid endpoint |
| Username | Free DNS Afraid username |
| Password | Free DNS Afraid password |
| Company Name | Your nompany name |
| Maintainer Email | Maintainer email or your company |
| Active | Flag that this Free DNS Afraid account is active or not |
Network Setting is a configuration to manage network from OTP-Pi. OTP-Pi is equipped with an access point so that it can be accessed directly using a laptop or cellphone without having to plug it into a wired network. This will make it easier for users because the user's LAN network configuration is different. Users simply set the IP address on the ethernet network according to the LAN network configuration used.
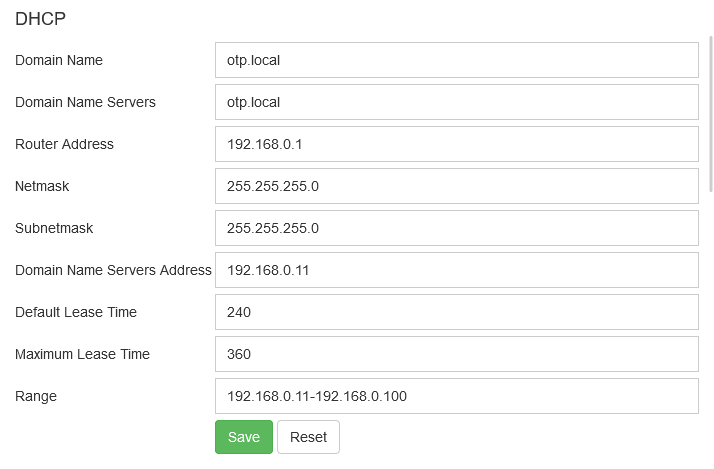
The DHCP configuration will set up DHCP on the OTP-Pi access point.
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Domain Name | Domain name of DHCP |
| Domain Name Servers | Domain name servers of DHCP |
| Router Address | Router address of DHCP |
| Netmask | Netmask of DHCP |
| Subnetmask | Subnetmask of DHCP |
| Domain Name Servers Address | Domain Name Servers Address of DHCP |
| Default Lease Time | Default lease time of the clients |
| Maximum Lease Time | Maximum lease time of the clients |
| Range | Allocated IP address range |
Example
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Domain Name | otppi.lan |
| Domain Name Servers | ns1.otppi.lan, ns2.otppi.lan |
| Router Address | 192.168.0.1 |
| Netmask | 255.255.255.0 |
| Subnetmask | 255.255.255.0 |
| Domain Name Servers Address | 192.168.0.11 |
| Default Lease Time | 3600 |
| Maximum Lease Time | 7200 |
| Range | 192.168.0.10-192.168.0.100, 192.168.0.110-192.168.0.200 |
The configuration above will create file /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf with its content as follows:
option domain-name "otppi.lan";
option domain-name-servers ns1.otppi.lan, ns2.otppi.lan;
default-lease-time 3600;
max-lease-time 7200;
authoritative;
subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers 192.168.0.1;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option domain-search "otppi.lan";
option domain-name-servers 192.168.0.11;
range 192.168.0.10 192.168.0.100;
range 192.168.0.110 192.168.0.200;
}
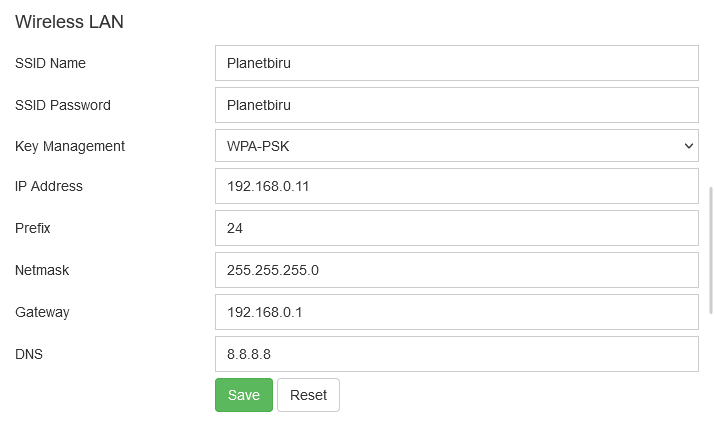
Wireless LAN configuration will set the IP address on the OTP-Pi wireless network. The default IP address of the OTP-Pi is 192.168.0.11
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| SSID Name | SSID name |
| SSID Password | SSID password |
| Key Management | Key management |
| IP Address | IP address of the device if client connect via Wifi |
| Prefix | Nework prefix |
| Netmask | Netmask |
| Gateway | Gateway |
| DNS | DNS |
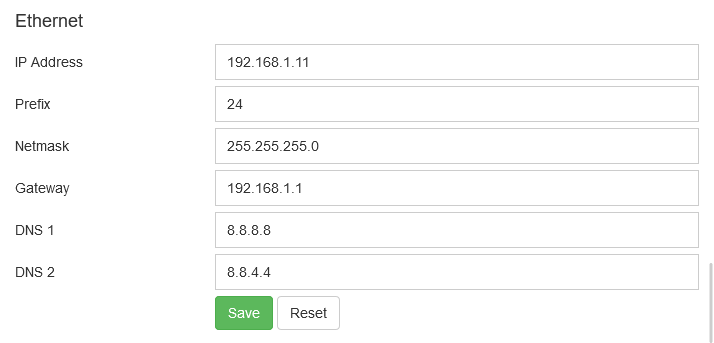
The Ethernet configuration will set the ethernet IP address on the OTP-Pi.
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| IP Address | IP address of the device if client connect via Ethernet |
| Prefix | Nework prefix |
| Netmask | Netmask |
| Gateway | Gateway |
| DNS1 | DNS 1 |
| DNS2 | DNS 2 |
OTP-Pi can open and close ports of the operating system used by SMS Broker. Closing this port will create a firewall at the operating system layer. In this case, if the port is closed, the equest will not reach the application.
The monitor can be used to view the activity of the modem installed on the OTP-Pi. When the OTP-Pi sends an SMS, the OTP-Pi will show where the SMS request came from and which modem was used. In addition, the status of the modem will be shown so that it will be seen which modems are connected correctly.
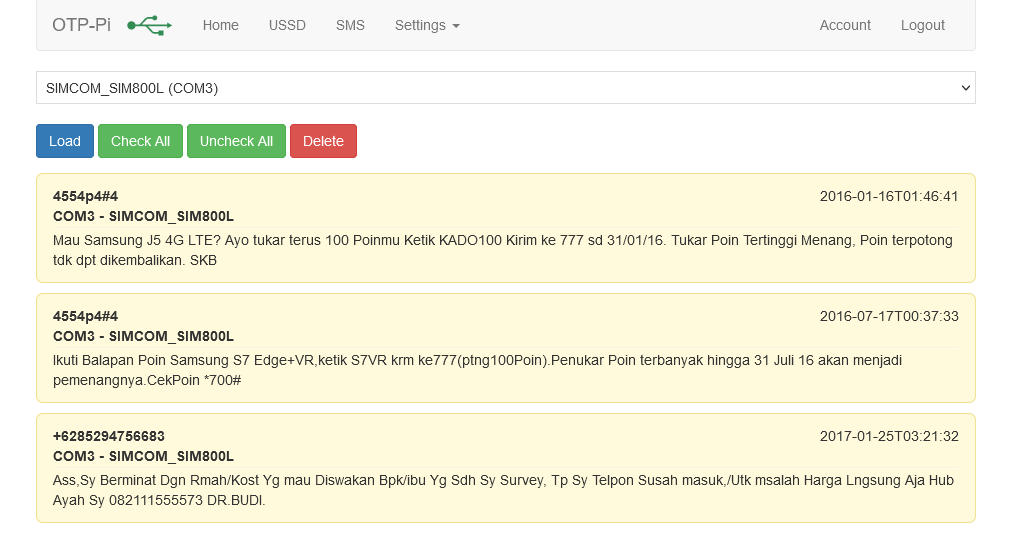
OTP-Pi provides a feature to read incoming SMS. The OTP-Pi will read all the SMS on the SIM card and move them to the storage on the device.
Users can delete the SMS when it is no longer needed. Users can also reply to the SMS manually from the OTP-Pi.
OTP-Pi provides a tool to change the IMEI of the modem. This tool is very useful for users who want to change IMEI for some reason. Users can directly enter the new IMEI and save it. The new IMEI will be written on the modem chip. Restarting the device may be required to implement the new IMEI on the GSM network.
OTP-Pi provides tools to create or delete sim card PIN. This tool is very useful when the user chooses to use or not to use the PIN on the sim card.
The Real Time Clock or RTC module is required to keep the device time when the device is turned off and not connected to the internet. The device must use the correct time so that the cookies sent by the device are not deleted by the browser due to expiration so that the administrator can manage the device including making settings. In addition, the device needs to record the time when an error occurred so that the error log can be read by the user for mitigation.
The Real Time Clock module is built into the device and is programmed to work as intended. If the device is off for a long time causing the RTC battery to run out, the device can adjust the time according to the browser that accesses it regardless of the time zone used. Furthermore, the administrator can set the device time if needed.
In case the user cannot access the administration web, either because he forgot his password, or because the network configuration is messed up, the user can reset the device. Reset the device is done by plugging in a flash disk containing the following file:
/otppi/reset-config.ini
Directory name, file name and extension must be written correctly in lower case. The /otppi/reset-config.ini file should contain the following text:
VERIFY = eyJkZXZpY2VUeXBlIjoiUlBpIiwgImJhc2VOYW1lIjoicmVzZXQtY29uZmlnLmluaSJ9
RESET_DHCP = true
RESET_WLAN = true
RESET_ETHERNET = true
RESET_USER = true
RESET_API = false
RESET_API_USER = false
RESET_BLOCKING = false
RESET_DDNS = false
RESET_EMAIL = false
RESET_SUBSCRIBER_AMQP = false
RESET_SUBSCRIBER_MQTT = false
RESET_SUBSCRIBER_REDIS = false
RESET_SUBSCRIBER_ACTIVEMQ = false
RESET_SUBSCRIBER_STOMP = false
RESET_SUBSCRIBER_WS = false
RESET_FIREWALL = false
RESET_KEYSTORE = false
RESET_MODEM = false
RESET_SMS = false
RESET_SMTP = false
RESET_VENDOR_AFRAID = false
RESET_VENDOR_CLOUDFLARE = false
RESET_VENDOR_DYNU = false
RESET_VENDOR_NOIP = falseVERIFY must be set with eyJkZXZpY2VUeXBlIjoiUlBpIiwgImJhc2VOYW1lIjoicmVzZXQtY29uZmlnLmluaSJ9. Other configuration properties must be set with true or false. true means that you will reset the configuration and false means that you will not reset the configuration.
Reset device will do the following things:
A. Basic Configuration
- RESET_DHCP (Restore the DHCP configuration to the default)
- RESET_WLAN (Restore the Wireless LAN configuration to the default)
- RESET_ETHERNET (Restore the LAN configuration to the default)
- RESET_USER (Delete all administrator accounts)
B. Advanced Configuration
- RESET_API
- RESET_API_USER
- RESET_BLOCKING
- RESET_DDNS
- RESET_EMAIL
- RESET_SUBSCRIBER_AMQP
- RESET_SUBSCRIBER_MQTT
- RESET_SUBSCRIBER_REDIS
- RESET_SUBSCRIBER_ACTIVEMQ
- RESET_SUBSCRIBER_STOMP
- RESET_SUBSCRIBER_WS
- RESET_FIREWALL
- RESET_KEYSTORE
- RESET_MODEM
- RESET_SMS
- RESET_SMTP
C. Vendor Configuration
- RESET_VENDOR_AFRAID
- RESET_VENDOR_CLOUDFLARE
- RESET_VENDOR_DYNU
- RESET_VENDOR_NOIP
To reset the device, perform the following steps:
- Prepare a flash disk with files as described above
- Unplug all modems installed on the device
- Insert the flash disk in any USB port of the device
- Unplug the power supply to the device
- Reconnect the power supply to the device
- Wait up to 10 minutes
- Remove the flash disk from the device
- Reconnect the power supply to the device
- Enter the access point with the SSID and password as stated in the brochure using a smartphone or PC
- Open page 192.168.0.8888 with a browser using a smartphone or PC that has been connected to the access point above
- Login to the page provided
- Create a new administrator for the device
Both WebSocket and Message Broker use a topic that can be configured from both sides (sender and receiver).
To use WebSocket, please use the WSMessageBrocker library with the link https://github.com/kamshory/OTP-Publisher or you can create your own.
To use RabbitMQ, please open the link https://www.rabbitmq.com/
To use Redis, please open the link https://redis.io/
To use Mosquitto, please open the link https://mosquitto.org/
In this scenario, the App Server can directly send the OTP to the OTP-Pi via HTTP.
Users can use a cheap domain and use the Dynamic Domain Name System for free. With the use of port forwarding on the router, OTP-Pi can be accessed from anywhere using a domain or subdomain. In this scenario, the user needs:
- OTP-Pi
- Fixed internet connection with public IP (static or dynamic)
- Router that can do port forwarding
- Domains whose name servers can be set
- Dynamic DNS service (free or paid)
In this scenario, the application server can generate and validate the OTP sent for each transaction. OTP creation and validation requires the following parameters:
reference
reference is unique transaction reference number. This number must be different from one transaction to another. This number is the key to validate the OTP.
receiver
receiver is the phone number or email address of the recipient.
param1, param2, param3, param4
These four parameters are additional information for validating the OTP. These four parameters must be the same between OTP creation and validation. Of course this parameter can be filled with empty strings. Information that can be used as this parameter is for example the sender's account number, the recipient's account number, the transaction amount (in string format), and so on.
OTP-Pi does not store the clear OTP but only stores the hash. In addition, the OTP-Pi immediately deletes the SMS sent immediately after. Thus, the OTP is very safe because it is only known by the recipient.
1. Message Format
Create OTP Request
POST /api/otp HTTP/1.1
Host: sub.domain.tld
Connection: close
User-agent: KSPS
Content-type: application/json
Content-length: 313
Authorization: Basic dXNlcjpwYXNzd29yZA==
{
"command": "request-otp",
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"expiration": 1629685838,
"receiver": "08126666666",
"message": "Your OTP is %s",
"reference": "12345678901234567890",
"param1": "100000",
"param2": "1234567890",
"param3": "987654",
"param4": "674527846556468254"
}
}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | String | Command for OTP-Pi |
| data | Object | Data for OTP-Pi |
data.date_time |
Number | Unix Time Stamp when the message is transmitted by the applications |
data.receiver |
String | MSISDN of the receiver |
data.message |
String | Content format of the SMS. Note that the format must be contains one %s |
data.reference |
String | Reference ID of the transaction. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
data.param1 |
String | Parameter 1. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
data.param2 |
String | Parameter 2. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
data.param3 |
String | Parameter 3. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
data.param4 |
String | Parameter 4. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
Create OTP Response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Host: sub.domain.tld
Connection: close
Content-type: application/json
Content-length: 199
{
"command": "request-otp",
"response_code": "0000",
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"receiver": "08126666666",
"reference": "12345678901234567890"
}
}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | String | Command for OTP-Pi |
| response_code | String | Response Code |
| data | Object | Data for OTP-Pi |
data.date_time |
Number | Unix Time Stamp when the message is transmitted by the applications |
data.receiver |
String | MSISDN of the receiver |
data.reference |
String | Reference ID of the transaction. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
Validate OTP Request
POST /api/otp HTTP/1.1
Host: sub.domain.tld
Connection: close
User-agent: KSPS
Content-type: application/json
Content-length: 274
Authorization: Basic dXNlcjpwYXNzd29yZA==
{
"command": "verify-otp",
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"receiver": "08126666666",
"otp": "123456",
"reference": "12345678901234567890",
"param1": "100000",
"param2": "1234567890",
"param3": "987654",
"param4": "674527846556468254"
}
}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | String | Command for OTP-Pi |
| data | Object | Data for OTP-Pi |
data.date_time |
Number | Unix Time Stamp when the message is transmitted by the applications |
data.receiver |
String | MSISDN of the receiver |
data.otp |
String | Cleat OTP to be valieadted |
data.reference |
String | Reference ID of the transaction. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
data.param1 |
String | Parameter 1. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
data.param2 |
String | Parameter 2. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
data.param3 |
String | Parameter 3. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
data.param4 |
String | Parameter 4. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
Validate OTP Response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Host: sub.domain.tld
Connection: close
Content-type: application/json
Content-length: 201
{
"command": "verify-otp",
"response_code": "0000",
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"receiver": "08126666666",
"reference": "12345678901234567890"
}
}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | String | Command for OTP-Pi |
| response_code | String | Response Code |
| data | Object | Data for OTP-Pi |
data.date_time |
Number | Unix Time Stamp when the message is transmitted by the applications |
data.receiver |
String | MSISDN of the receiver |
data.reference |
String | Reference ID of the transaction. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
Send SMS Request
POST /api/sms HTTP/1.1
Host: sub.domain.tld
Connection: close
User-agent: KSPS
Content-type: application/json
Content-length: 182
Authorization: Basic dXNlcjpwYXNzd29yZA==
{
"command": "send-sms",
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"expiration": 1629685838,
"id": 123456,
"receiver": "08126666666",
"message": "Your OTP is 1234"
}
}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | String | Command for OTP-Pi |
| data | Object | Data for OTP-Pi |
data.date_time |
Number | Unix Time Stamp when the message is transmitted by the applications |
data.id |
String | SMS ID |
data.reference |
String | Reference ID of the transaction. This value must match between Create OTP and Validate OTP |
data.receiver |
String | MSISDN of the receiver |
data.message |
String | Content of the SMS |
Send Email Request
POST /api/sms HTTP/1.1
Host: sub.domain.tld
Connection: close
User-agent: KSPS
Content-type: application/json
Content-length: 222
Authorization: Basic dXNlcjpwYXNzd29yZA==
{
"command": "send-email",
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"expiration": 1629685838,
"id": 123456,
"receiver": "someone@domain.tld",
"subject": "Your OTP Code",
"message": "Your OTP is 1234"
}
}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | String | Command for OTP-Pi |
| data | Object | Data for OTP-Pi |
data.date_time |
Number | Unix Time Stamp when the message is transmitted by the applications |
data.id |
String | SMS ID |
data.receiver |
String | Recipient's email address |
data.message |
String | Content of the SMS |
Block Number Request
POST /api/block HTTP/1.1
Host: sub.domain.tld
Connection: close
User-agent: KSPS
Content-type: application/json
Content-length: 107
Authorization: Basic dXNlcjpwYXNzd29yZA==
{
"command": "block-msisdn",
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"receiver": "08126666666"
}
}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | String | Command for OTP-Pi |
| data | Object | Data for OTP-Pi |
data.date_time |
Number | Unix Time Stamp when the message is transmitted by the applications |
data.msisdn |
String | MSISDN number to block |
Unblock Number Request
POST /api/unblock HTTP/1.1
Host: sub.domain.tld
Connection: close
User-agent: KSPS
Content-type: application/json
Content-length: 109
Authorization: Basic dXNlcjpwYXNzd29yZA==
{
"command": "unblock-msisdn",
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"receiver": "08126666666"
}
}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | String | Command for OTP-Pi |
| data | Object | Data for OTP-Pi |
data.date_time |
Number | Unix Time Stamp when the message is transmitted by the applications |
data.receiver |
String | MSISDN number to be unblocked |
Get Modem List Request
POST /api/modem HTTP/1.1
Host: sub.domain.tld
Connection: close
User-agent: KSPS
Content-type: application/json
Content-length: 87
Authorization: Basic dXNlcjpwYXNzd29yZA==
{
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778
},
"command": "get-modem-list"
}
Get Modem List Response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Sun, 18 Oct 2012 10:36:20 GMT
Server: Apache/2.2.14
Content-Length: 1192
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Connection: Closed
{
"response_code": "0000",
"data": {
"modem_list": {
"d740eb1f5e9799c2b50452ea5acf6054": {
"internetConnected": false,
"active": true,
"imsi": "990106913401164",
"smsCenter": "",
"copsOperator": "TELKOMSEL",
"connected": false,
"iccid": "89621010691340116477",
"defaultModem": true,
"internetAccess": false,
"port": "COM7",
"name": "SIMCOM_SIM800L",
"imei": "359848091599999",
"id": "d740eb1f5e9799c2b50452ea5acf6054"
},
"20570ff7f9a4664df11e8c3dfdf4c6c4": {
"internetConnected": false,
"active": true,
"imsi": "880106913401164",
"smsCenter": "",
"copsOperator": "TELKOMSEL",
"connected": false,
"iccid": "89621010691340116454",
"defaultModem": false,
"internetAccess": false,
"port": "COM3",
"name": "Huawei",
"imei": "359848091599994",
"id": "20570ff7f9a4664df11e8c3dfdf4c6c4"
}
}
},
"command": "get-modem-list"
}
USSD Command Request
Users can run USSD code via the API either using the REST API or using the message broker. When executing the USSD code, the user must submit the modem ID. The modem ID can be obtained using the API either using the REST API or using a message broker.
POST /api/ussd HTTP/1.1
Host: sub.domain.tld
Connection: close
User-agent: KSPS
Content-type: application/json
Content-length: 163
Authorization: Basic dXNlcjpwYXNzd29yZA==
{
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"modem_id": "d740eb1f5e9799c2b50452ea5acf6054",
"ussd_code": "*888#"
},
"command": "request-ussd"
}
USSD Command Response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Sun, 18 Oct 2012 10:36:20 GMT
Server: Apache/2.2.14
Content-Length: 220
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Connection: Closed
{
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"modem_id": "d740eb1f5e9799c2b50452ea5acf6054",
"ussd_code": "*888#",
"ussd_response": "Sisa pulsa Anda adalah Rp 12345"
},
"command": "request-ussd",
}
2. Authorization
OTP-Pi use Basic Authorization. Username and password required on each reaquest.
For more information, click https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Authorization
In this scenario, the App Server may send the OTP to RabbitMQ Server, Redis Server, Mosquitto Server, ActiveMQ Server or WSMessageBroker. WSMessageBroker uses the WebSoket protocol and Basic Authentication. Both App Server and OTP-Pi act as clients of WSMessageBroker.
In this scenario, the application cannot request the OTP-Pi to validate the previously sent OTP. Thus, the application must have its own OTP system. The application simply sends a message containing the OTP. The application must have a mechanism to validate the previously submitted OTP.
Another way is to use a separate OTP system from the application. It is this system that issues the OTP code so that it can validate the code if the application so desires.
App Server acts as publisher and OTP-Pi becomes consumer of RabbitMQ Server, Redis Server, Mosquitto Server, ActiveMQ Server or WSMessageBroker. Both must use the same topic so that all OTPs sent by the App Server can be received by the OTP-Pi.
From the two scenarios above, the OTP-Pi will send SMS using a GSM modem that is physically attached to the OTP-Pi device. Users can use either RabbitMQ Server, Redis Server, Mosquitto Server, ActiveMQ Server or WSMessageBroker can also use both at the same time. However, if the App Server sends the same OTP to RabbitMQ Server, Redis Server, Mosquitto Server, ActiveMQ Server or WSMessageBroker, the OTP-Pi will send the SMS twice to the recipient number.
In this scenario, the user does not need a public IP. Users only need:
- OTP-Pi
- Internet connection (no need for public IP and port forwarding)
- RabbitMQ, Redis, Mosquitto, ActiveMQ, Stomp or WSMessageBroker servers
1. Message Format
Send SMS Request
{
"command": "send-sms",
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"expiration": 1629685838,
"id": 123456,
"receiver": "08126666666",
"message": "Your OTP is 1234"
}
}| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | String | Command for OTP-Pi |
| data | Object | Data for OTP-Pi |
data.date_time |
Number | Unix Time Stamp when the message is transmitted by the applications |
data.id |
String | SMS ID |
data.receiver |
String | MSISDN of the receiver |
data.message |
String | Content of the SMS |
Send Email Request
{
"command": "send-email",
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"expiration": 1629685838,
"id": 123456,
"receiver": "someone@domain.tld",
"subject": "Your OTP Code",
"message": "Your OTP is 1234"
}
}| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | String | Command for OTP-Pi |
| data | Object | Data for OTP-Pi |
data.date_time |
Number | Unix Time Stamp when the message is transmitted by the applications |
data.id |
String | SMS ID |
data.receiver |
String | Recipient's email address |
data.message |
String | Content of the SMS |
Block Number Request
{
"command": "block-msisdn",
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"receiver": "08126666666",
}
}| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | String | Command for OTP-Pi |
| data | Object | Data for OTP-Pi |
data.date_time |
Number | Unix Time Stamp when the message is transmitted by the applications |
data.receiver |
String | MSISDN number to block |
Unblock Number Request
{
"command": "unblock-msisdn",
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"receiver": "08126666666",
}
}| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | String | Command for OTP-Pi |
| data | Object | Data for OTP-Pi |
data.date_time |
Number | Unix Time Stamp when the message is transmitted by the applications |
data.receiver |
String | MSISDN number to be unblocked |
Get Modem List Request
{
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778
},
"command": "get-modem-list",
"callback_topic": "random_topic",
"callback_delay": 50
}
Get Modem List Response
{
"response_code": "0000",
"data": {
"modem_list": {
"d740eb1f5e9799c2b50452ea5acf6054": {
"internetConnected": false,
"active": true,
"imsi": "990106913401164",
"smsCenter": "",
"copsOperator": "TELKOMSEL",
"connected": false,
"iccid": "89621010691340116477",
"defaultModem": true,
"internetAccess": false,
"port": "COM7",
"name": "SIMCOM_SIM800L",
"imei": "359848091599999",
"id": "d740eb1f5e9799c2b50452ea5acf6054"
},
"20570ff7f9a4664df11e8c3dfdf4c6c4": {
"internetConnected": false,
"active": true,
"imsi": "880106913401164",
"smsCenter": "",
"copsOperator": "TELKOMSEL",
"connected": false,
"iccid": "89621010691340116454",
"defaultModem": false,
"internetAccess": false,
"port": "COM3",
"name": "Huawei",
"imei": "359848091599994",
"id": "20570ff7f9a4664df11e8c3dfdf4c6c4"
}
}
},
"command": "get-modem-list"
}USSD Command Request
Users can run USSD code via the API either using the REST API or using the message broker. When executing the USSD code, the user must submit the modem ID. The modem ID can be obtained using the API either using the REST API or using a message broker.
{
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"modem_id": "d740eb1f5e9799c2b50452ea5acf6054",
"ussd_code": "*888#"
},
"command": "request-ussd",
"callback_topic": "random_topic",
"callback_delay": 50
}
USSD Command Response
{
"data": {
"date_time": 1629685778,
"modem_id": "d740eb1f5e9799c2b50452ea5acf6054",
"ussd_code": "*888#",
"ussd_response": "Sisa pulsa Anda adalah Rp 12345"
},
"command": "request-ussd",
"callback_topic": "random_topic",
"callback_delay": 50
}
2. Websocket Handshakes
The handshake between OTP-Pi and WSMessageBroker is as follows:
- OTP-Pi as client and WSMessageBroker as server
- OTP-Pi sends request to WSMessageBroker
WebSocket Subscriber Configuration Example
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Host | domain.example |
| Port | 8000 |
| Path | /ws |
| Username | username |
| Password | password |
| Topic | sms |
Example of a WebSocket Handshake
GET /ws?topic=sms HTTP/1.1
Host: domain.example:8000
Authorization: Basic dXNlcm5hbWU6cGFzc3dvcmQ=
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: Upgrade
Sec-WebSocket-Key: dGhlIHNhbXBsZSBub25jZQ==
Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13
The server will verify whether the username and password are correct. If true, the server will add the connection to the list of recipients of the message.
When a client sends a message, the message will be sent to all clients by topic except the sender. Thus, the handshake between the sender and the recipient of the message is the same.
The OTP-Pi never sends messages to the WSMessageBroker server. OTP-Pi only accepts messages according to the desired topic.