This repository is the ROS2 driver for ADI_IMU.
Click here for ROS1 version.
“TR-IMU1647X” is Analog Devices IMU sensor that can be easily connected to ROS and output high-precision attitude angles.
Click the thumbnail to open the youtube video.
This software is compatible with these sensors.
- TR-IMU16470
- TR-IMU16475-2
- TR-IMU16477-2
- TR-IMU16495-2
- TR-IMU16500
- TR-IMU16505-2
- TR-IMU-Platform
This software has been confirmed to work on the following OS and ROS versions.
- Ubuntu 18.04 LTS + ros2 dashing (This is not maintained. If you use it, use the dashing_eloquent branch.)
- Ubuntu 18.04 LTS + ros2 eloquent (This is not maintained. If you use it, use the dashing_eloquent branch.)
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS + ros2 foxy or galactic (Use the foxy_galactic branch.This is not maintained. If you use it, use the foxy_galactic branch.)
- Ubuntu 22.04 LTS + ros2 humble (Use the humble branch.)
- Ubuntu 24.04 LTS + ros2 jazzy (Use the jazzy branch.)
Add the user to the dialout group to use the USB port as the login user. (If you have already added it, skip this item) Execute the following command.
$ sudo addgroup `whoami` dialout
Then, log out and log in again to reflect the settings.
First, set the DIP switch.
- For TR-IMU16470 or TR-IMU16475-2, turn on No. 1 and No. 4 and turn off all the rest.
- For TR-IMU-Platform, turn on No. 1 and No. 5 and turn off all the rest.
After setting the switch, connect the sensor via USB.
Go to your package directory and clone.
$ cd [your package directory]
$ git clone --recursive https://github.com/technoroad/ADI_IMU_TR_Driver_ROS2
Then resolve dependencies.
$ cd [your workspace directory]
$ rosdep update
$ rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src --rosdistro ${ROS_DISTRO} -y
Go to your workspace directory and run the build command.
$ cd [your workspace directory]
$ colcon build --symlink-install
Then set the path and configure out put.
$ source ./install/setup.bash
This software has two execution modes.
- Imu board(On-board angle estimation) + Rviz2 vizualization
- Imu board(Acceleration and gyro output)
The respective execution methods are shown below.
Execute the following command.
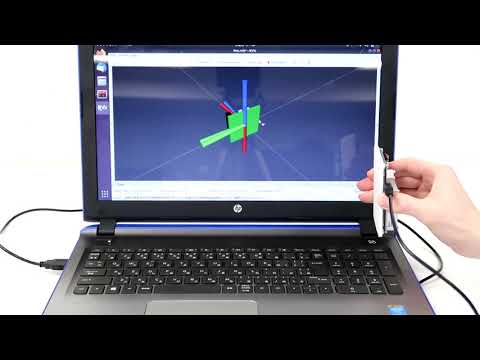
$ ros2 launch adi_imu_tr_driver_ros2 adis_rcv_csv.launch.py mode:=Attitude device:=/dev/ttyACM0
You can see the model of ADIS16470 breakout board in rviz2 panel.
Execute the following command.
$ ros2 launch adi_imu_tr_driver_ros2 adis_rcv_csv.launch.py mode:=Register device:=/dev/ttyACM0
Then you can see the output with the following command.
$ ros2 topic echo /imu/data_raw
・・・
angular_velocity:
x: -0.0116995596098
y: -0.00314657808936
z: 0.000579557116093
angular_velocity_covariance: [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
linear_acceleration:
x: 0.302349234658
y: -0.303755252655
z: 9.87837325989
linear_acceleration_covariance: [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
・・・
This software outputs the following topics.
-
/imu/data_raw (sensor_msgs/Imu)
IMU raw output. It contains angular velocities and linear accelerations. The orientation is always unit quaternion. To view this data, execute sensor in the Register mode. example:
$ ros2 topic echo /imu/data_raw
・・・
angular_velocity:
x: -0.0116995596098
y: -0.00314657808936
z: 0.000579557116093
angular_velocity_covariance: [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
linear_acceleration:
x: 0.302349234658
y: -0.303755252655
z: 9.87837325989
linear_acceleration_covariance: [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
・・・
-
/diagnostics (diagnostic_msgs/DiagnosticArray)
Sensor state output. example:
$ ros2 topic echo /diagnostics
・・・
header:
seq: 80
stamp:
secs: 1587104853
nsecs: 921894057
frame_id: ''
status:
-
level: 0
name: "adis_rcv_csv_node: imu"
message: "OK"
hardware_id: "ADIS16470"
values: []
・・・
How to update the calibration parameters.
- Start the sensor in attitude mode using the following command.
$ ros2 launch adi_imu_tr_driver_ros2 adis_rcv_csv.launch.py mode:=Attitude device:=/dev/ttyACM0
- Leave the sensor stationary for 120 seconds. (Parameters are calculated automatically)
- Update the parameters with the following command.
ros2 service call /imu/cmd_srv adi_imu_tr_driver_ros2/srv/SimpleCmd "{cmd: 'START_BIAS_CORRECTION', args: []}"
How to reset the attitude angle.
- Start the sensor in attitude mode using the following command.
$ ros2 launch adi_imu_tr_driver_ros2 adis_rcv_csv.launch.py mode:=Attitude device:=/dev/ttyACM0
- Leave the sensor stationary for 120 seconds. (Parameters are calculated automatically)
- Update the parameters with the following command.
$ ros2 service call /imu/cmd_srv adi_imu_tr_driver_ros2/srv/SimpleCmd "{cmd: 'RESET_FILTER', args: []}"
How to get error code
- Get error code from sensor.
$ ros2 service call /imu/cmd_srv adi_imu_tr_driver_ros2/srv/SimpleCmd "{cmd: 'error', args: []}"
- Get error code description.
$ ros2 service call /imu/cmd_srv adi_imu_tr_driver_ros2/srv/SimpleCmd "{cmd: 'help', args: []}"
※ Sending the help command stops data transmission from IMU.Send the start command to resume.
$ ros2 service call /imu/cmd_srv adi_imu_tr_driver_ros2/srv/SimpleCmd "{cmd: 'start', args: []}"
MIT