This lab allows you to practice and apply the concepts and techniques taught in class.
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to:
-
Design and implement a database schema that accurately represents the relationships between the data sources and allows for efficient querying and analysis.
-
Use appropriate SQL commands to load the data into the database, ensuring data integrity and consistency.
Before this starting this lab, you should have learnt about:
-
Fundamental concepts of database design, including entities, attributes, primary keys, and foreign keys.
-
Basic comprehension of SQL syntax and statements, such as CREATE, INSERT INTO, UPDATE, and DELETE.
-
Familiarity with the concept of NOT NULL constraints and data types in SQL.
Welcome to this lab where you will practice how to design, create and manage a database. In this lab, you will act as a data expert at a car dealership company which sells new cars of various brands and models. You have been assigned the task of designing, creating, and managing a database to keep records about cars, salespersons, customers, and invoices.
This lab consists of three challenges that will help you to achieve this task. In the first challenge, you will design the database by identifying the entities and their relationships. In the second challenge, you will create the database and tables using MySQL and the CREATE DATABASE and CREATE TABLE statements. Finally, in the third challenge, you will insert data into the tables using the INSERT INTO statement. In the bonus challenge, you will update data using the UPDATE statement and delete data using the DELETE statement.
By completing this lab, you will gain valuable experience in designing and creating a database, and managing data in a relational database management system. Let's get started!
Design an Entity-Relationship (E-R) diagram for your database.
The database should have at least four tables: cars, customers, salespersons and invoices.
The minimal information to be recorded is described below:
-
Cars - e.g. the vehicle identification number (VIN), manufacturer, model, year, and color of the cars in your company's inventory.
-
Customers - e.g. the customer ID, name, phone number, email, address, city, state/province, country, and zip/postal code of the customers.
-
Salespersons - e.g. staff ID, name, and the store at your company.
-
Invoices - e.g. the invoice number, date, car, customer, and salesperson related to each car sale.
When designing a database, it's important to consider several aspects to ensure its functionality and efficiency. Here are some things to keep in mind:
-
Entities and attributes
- Start by identifying the entities you need to store in your database and the attributes (or properties) that describe each entity.
- For each attribute, decide on the most appropriate data type to use.
- Determine which attributes are mandatory and which are optional.
- For each entity, you should also create an auto-increment numeric ID column using the
AUTO_INCREMENTfeature in MySQL.- The auto-increment ID should be different from the customer ID or staff ID.
-
Relations between entities
- Identify the relationships between the entities in your database. Decide if each relationship is a one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many relationship. One-to-one relationships occur when each entity in one table corresponds to exactly one entity in the other table. One-to-many relationships occur when each entity in one table corresponds to one or more entities in the other table. Many-to-many relationships occur when each entity in one table corresponds to multiple entities in the other table, and vice versa.
-
Primary keys and foreign keys
- Use primary keys and foreign keys to establish relationships between the entities in your database.
- Primary keys are unique identifiers for each entity in a table, and are used to link entities in different tables together.
- Foreign keys are used to reference the primary key of another table, creating a relationship between the two tables.
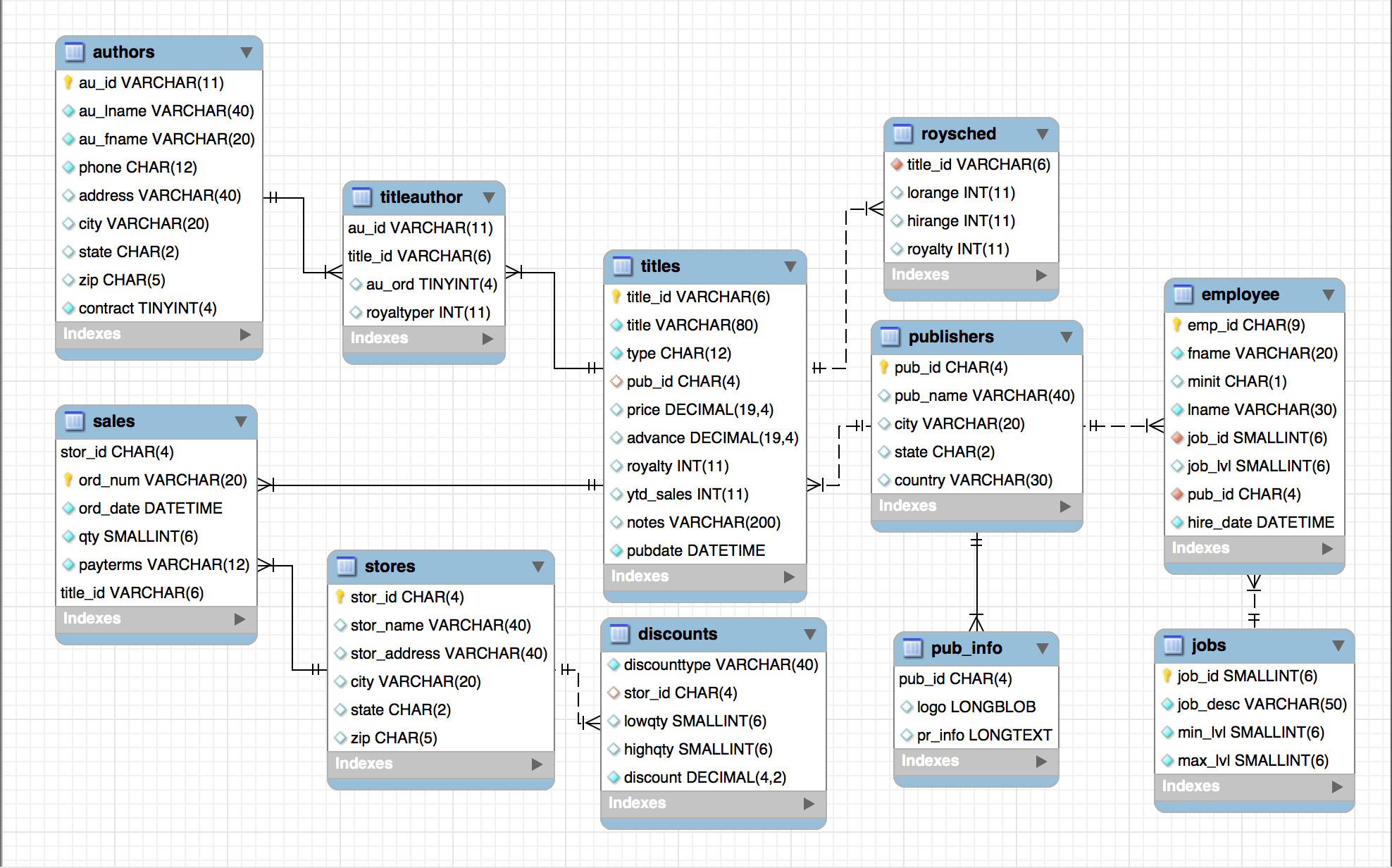
Your end product of this challenge should look something like the E-R diagram shown below, although it doesn't have to be that complicated:
Using pen and paper (or computer software if you are skilled at creating digital diagrams), design a database to meet the minimum requirements of the task.
In this challenge, you will create the database and tables based on the database design you created in Challenge 1.
-
Open MySQL Workbench.
-
Create a new file named
create.sql. -
Create a MySQL database for this lab using SQL Query Script in MySQL Workbench. You can execute the following code:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS lab_mysql; USE lab_mysql;
-
Write SQL queries to create the tables and columns based on your database design.
You will use the
CREATE TABLEstatement for this purpose. You can find the reference for theCREATE TABLEstatement here.To test your
CREATE TABLEstatement, you should add aDROP TABLEstatement above eachCREATE TABLEstatement in your script, like this:DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cars; CREATE TABLE cars ( ... );
Make sure to end each statement with a semicolon.
-
Save the
create.sqlfile and execute it to create the database and tables.
The purpose of database seeding is to provide some initial data for an empty database to start software development based on that data.
Here are some instructions to seed your database:
-
Open MySQL Workbench and connect the database to where you want to seed the data.
-
Create a new file named
seeding.sql. -
Use the
INSERT INTOstatement to insert data into your database. For example:INSERT INTO users (id, name, email) VALUES (1, 'John Doe', 'johndoe@example.com'), (2, 'Jane Smith', 'janesmith@example.com'), (3, 'Bob Johnson', 'bobjohnson@example.com');
This would insert three records into the
userstable, with the specifiedid,name, andemailvalues.You can find more information on how to use
INSERT INTOhere. -
Save the
seeding.sqlfile and execute it to insert the data into your database. -
There is some sample dummy data for your convenience provided below, but please note that they may not be compatible with your specific database design. It is possible that you may need to modify them to fit the appropriate format.
| id | vin | manufacturer | model | year | color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3K096I98581DHSNUP | Volkswagen | Tiguan | 2019 | Blue |
| 2 | ZM8G7BEUQZ97IH46V | Peugeot | Rifter | 2019 | Red |
| 3 | RKXVNNIHLVVZOUB4M | Ford | Fusion | 2018 | White |
| 4 | HKNDGS7CU31E9Z7JW | Toyota | RAV4 | 2018 | Silver |
| 5 | DAM41UDN3CHU2WVF6 | Volvo | V60 | 2019 | Gray |
| 6 | DAM41UDN3CHU2WVF6 | Volvo | V60 Cross Country | 2019 | Gray |
| id | cust_id | cust_name | cust_phone | cust_email | cust_address | cust_city | cust_state | cust_country | cust_zipcode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10001 | Pablo Picasso | +34 636 17 63 82 | - | Paseo de la Chopera, 14 | Madrid | Madrid | Spain | 28045 |
| 1 | 20001 | Abraham Lincoln | +1 305 907 7086 | - | 120 SW 8th St | Miami | Florida | United States | 33130 |
| 2 | 30001 | Napoléon Bonaparte | +33 1 79 75 40 00 | - | 40 Rue du Colisée | Paris | Île-de-France | France | 75008 |
| id | staff_id | name | store |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 00001 | Petey Cruiser | Madrid |
| 2 | 00002 | Anna Sthesia | Barcelona |
| 3 | 00003 | Paul Molive | Berlin |
| 4 | 00004 | Gail Forcewind | Paris |
| 5 | 00005 | Paige Turner | Mimia |
| 6 | 00006 | Bob Frapples | Mexico City |
| 7 | 00007 | Walter Melon | Amsterdam |
| 8 | 00008 | Shonda Leer | São Paulo |
| id | invoice_number | date | car | customer | salesperson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 852399038 | 22-08-2018 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 731166526 | 31-12-2018 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| 3 | 271135104 | 22-01-2019 | 2 | 2 | 7 |
Congratulations on reaching the bonus challenge! In this challenge, you will update and delete database records.
To begin, you have been provided with the email addresses of three customers in the form of a table. Your task is to create an update.sql file that will update the existing data in your database with the new email addresses.
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Pablo Picasso | ppicasso@gmail.com |
| Abraham Lincoln | lincoln@us.gov |
| Napoléon Bonaparte | hello@napoleon.me |
Additionally, you have discovered a duplicated car entry with the VIN DAM41UDN3CHU2WVF6, and you want to remove the entry with car ID #4 from the database. You will need to create a delete.sql file to perform this deletion.
Hint: if you get an error You are using safe update mode while updating, you can fix it by desabling safe mode using SET SQL_SAFE_UPDATES = 0;
- Fork this repo
- Clone it to your machine
Complete the challenges in this readme. Follow the instructions and implement:
-
Your database design diagram in the form of image.
-
create.sqlandseeding.sql -
[OPTIONAL]
update.sqlanddelete.sql
- Upon completion, run the following commands:
git add .
git commit -m "Solved lab"
git push origin master- Create a Pull Request so that your TAs can check your work.