Fortran codes for computation of Earth’s rotation polar shift effects on all-element geodetic variations
https://www.zcyphygeodesy.com/en/h-nd-121.html
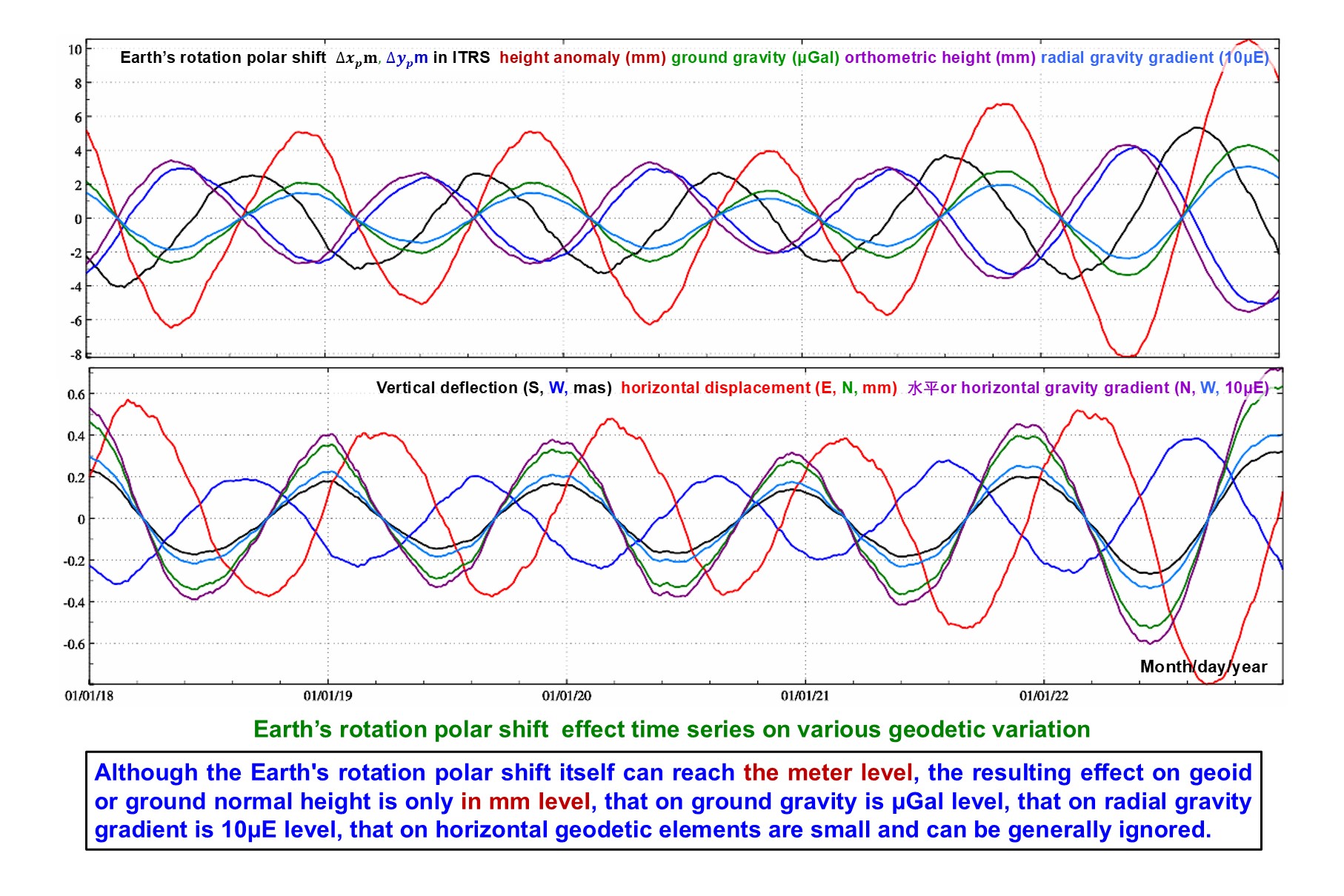
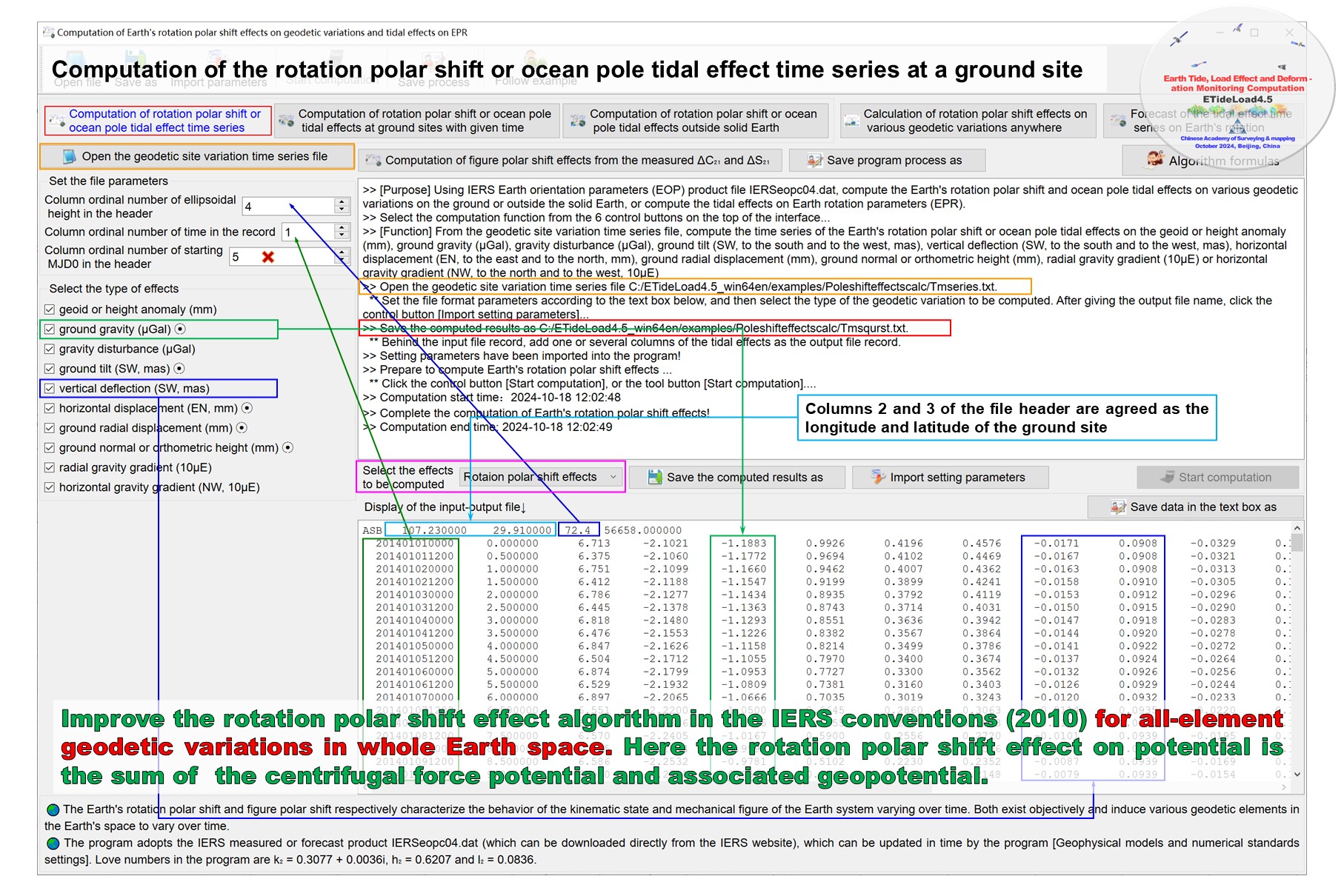
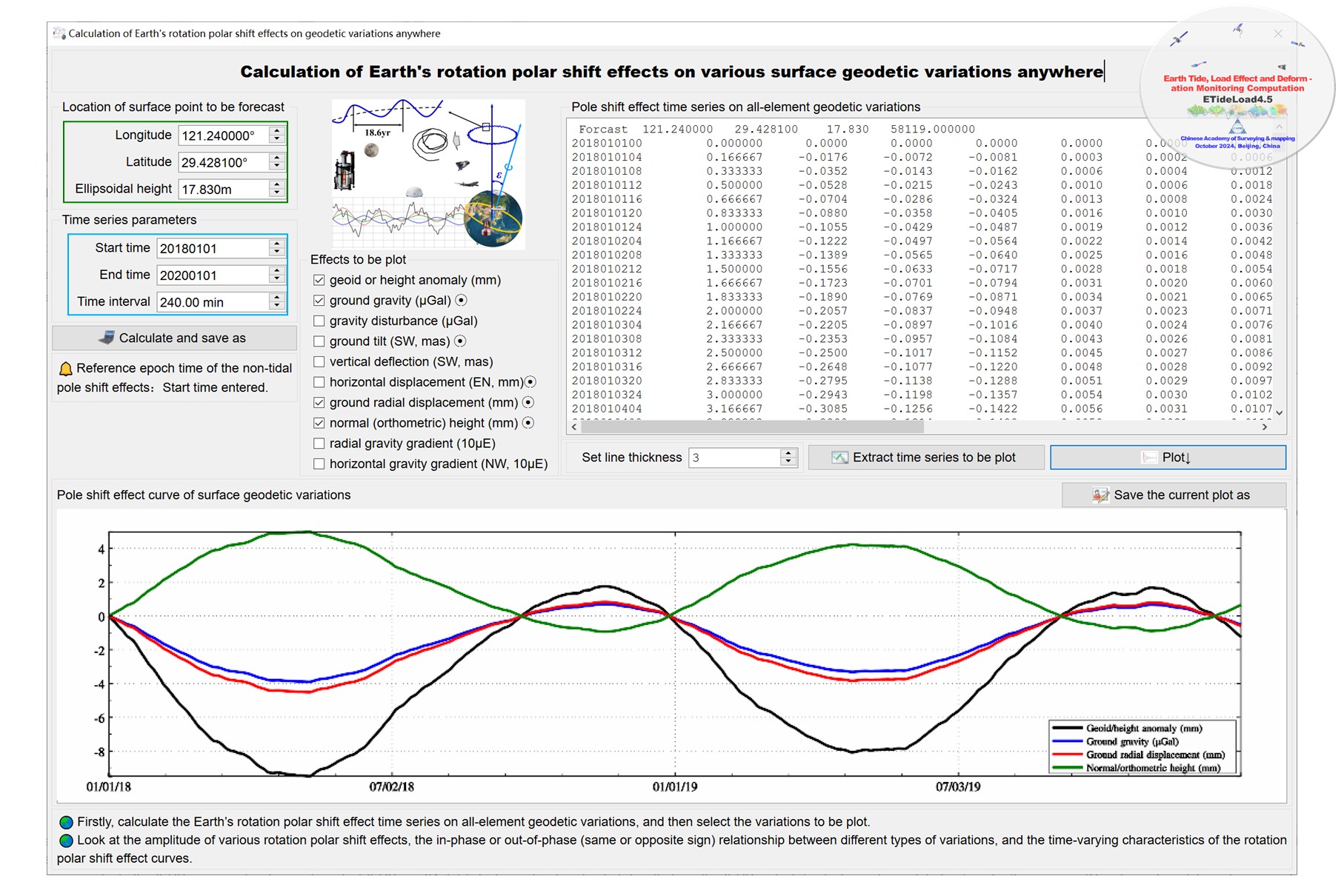
Given the longitude, latitude, ellipsoidal height and time of the calculation point, using IERS Earth orientation parameters (EOP) product file IERSeopc04.dat, compute the Earth’s rotation polar shift effects on the geoid or height anomaly (mm), ground gravity (μGal), gravity disturbance (μGal), ground tilt (SW, to the south and to the west, mas), vertical deflection (SW, to the south and to the west, mas), horizontal displacement (EN, to the east and to the north, mm), ground radial displacement (mm), ground normal or orthometric height (mm), radial gravity gradient (10μE) or horizontal gravity gradient (NW, to the north and to the west, 10μE).
Improve the Earth’s rotation polar shift effect algorithm in the IERS conventions (2010) for all-element geodetic variations in whole Earth space. Here the rotation polar shift effect on potential is the sum of the centrifugal force potential and associated geopotential.
tdn(14): the rotation polar shift effects on all-element geodetic variations.
tdn(1:14) stores the rotation polar shift effects on 10 kinds of geodetic variations, which are the solid tidal effects on height anomaly tdn(1) (mm), ground gravity #tdn(2) (μGal), gravity disturbance tdn(3) (μGal), ground tilt #tdn(4:5) (SW, to the south and to the west, mas), vertical deflection tdn(6:7) (SW, to the south and to the west, mas), horizontal displacement #tdn(8:9) (EN, to the east and to the north, mm), ground radial displacement #tdn(10) (mm), ground normal or orthometric height #tdn(11) (mm), radial gravity gradient tdn(12 )(10μE) or horizontal gravity gradient tdn(13:14) (NW, to the north and to the west, 10μE).
The calculation point can be on the ground, low altitude, satellite, ocean or underwater space. The geodetic variations abvove marked with # are valid only when the site is fixed with the solid Earth.
(1) The IERS Earth orientation parameters (EOP) time series file IERSeopc04.dat.
Rotapoleshifteffects.f90
The record of the test output file reslt.txt: the long integer time agreed by ETideLoad, difference between the MJD day and starting MJD0, tdn(1:14)
(1) Algorithm module for the Earth’s rotation polar shift effects on all-element geodetic variations.
PoleCalc(BLH,m1,m2,tdn,GRS)
Input parameters: BLH(3) - latitude, longitude (decimal degrees) and ellipsoidal height (m) at the calculation point.
Input parameters: m1,m2 - the Earth’s rotation polar shift parameters.
Input parameters: GRS(6) - gm, ae, j2, omega, 1/f, default value
Return parameters: tdn(1:14) - the Earth’s rotation polar shift effects on all-element geodetic variations.
GNormalfd(BLH, NFD, GRS)
Return parameters: NFD(5) - the normal geopotential (m2/s2), normal gravity (mGal), normal gravity gradient (E), normal gravity line direction (', expressed by its north declination relative to the center of the Earth center of mass) or normal gravity gradient direction (', expressed by its north declination relative to the Earth center of mass).
LegPn_dt2(pn,dp1,dp2,n,t) ! t=cos ψ
BLH_RLAT(GRS, BLH, RLAT); BLH_XYZ(GRS, BLH, XYZ);
RLAT_BLH(GRS, RLAT, BLH)
CAL2JD (IY0, IM0, ID0, DJM, J); JD2CAL(DJ1, DJ2, IY, IM, ID, FD, J)
PickRecord(str0, kln, rec, nn); tmcnt(tm, iyr, imo, idy, ihr, imn, sec)
mjdtotm(mjd0, ltm); tmtostr(tm, tmstr)
Fortran90, 132 Columns fixed format. Fortran compiler for any operating system. No external link library required.
[Algorithmic formula] ETideLoad4.5 User Reference https://www.zcyphygeodesy.com/en/
8.6.1 Earth’s rotation polar shift effects on geodetic variations
8.3.3 Legendre function and its first and second derivatives to ψ
The zip compression package includes the test project in visual studio 2017 - intel fortran integrated environment, DOS executable test file, geophysical models and all input and output data.